WHO Identifies 17 Top Priority Pathogens for New Vaccine Development

Powered by WPeMatico

Powered by WPeMatico

Powered by WPeMatico
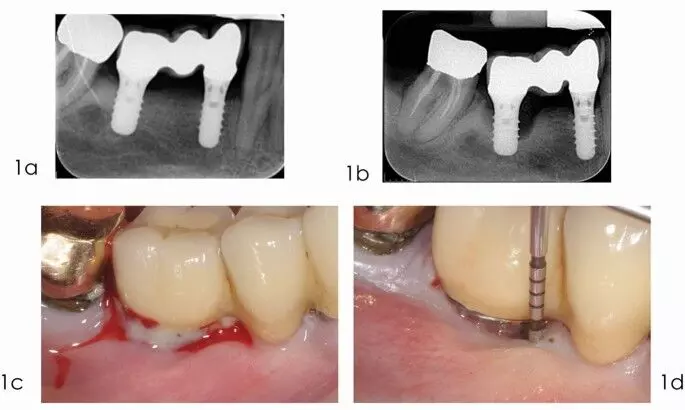
The submerged reconstructive approach significantly enhances clinical outcomes of surgical treatment of periimplantitis suggests a study published in the International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants.
A study was done to complete a reanalysis study of two similarly designed prospective controlled studies exploring prognostic factors associated with the surgical outcomes of reconstructive treatment of peri-implantitis. Materials and Methods: Individual patient data of both studies were gathered. The initial study employed a submerged healing approach via primary wound closure with implant suprastructure removal and complete coverage of grafted sites. The second study employed a nonsubmerged healing protocol in which healing abutments were kept in place and the implants were not fully submerged.
Both studies measured all prognostic factors at similar time points throughout 1 year and included clinical defect fill (DF) and radiographic defect fill (RDF), reduction of pocket depth (PDR), and bleeding on probing (BoP). Multilevel regression was used for statistical assessment of outcomes relative to the impact of site, local, surgical, and patient-related variables. Results: Overall, 59 implants (30 submerged and 29 nonsubmerged) were treated. Statistically significant higher DF (on average 0.9 mm higher), RDF (1.7 mm), and PDR (1.3 mm) were observed when a submerged reconstructive approach was performed, whereas BoP reduction was similar.
After controlling for treatment (submerged/ nonsubmerged), there were no other significant associations with patient-related (age, sex, smoking, prior periodontitis etc), or implant-related (previous prosthesis type, arch, keratinized tissue width [KTW], etc) factors. Within the study’s limitations, we conclude that a submerged reconstructive approach for surgical management of peri-implantitis leads to significantly enhanced clinical and radiographic outcomes when compared to a nonsubmerged approach.
Reference:
Wen SC, Sabri H, Dastouri E, Huang WX, Barootchi S, Wang HL. Submerged vs Nonsubmerged Reconstructive Approach for Surgical Treatment of Peri-implantitis: Reanalysis of Two Prospective Clinical Studies. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2024 Aug 29;39(4):526-536. doi: 10.11607/jomi.10560. PMID: 37939242.
Powered by WPeMatico
A new study published in the journal of Arthritis & Rheumatology showed that interstitial lung disease (ILD) can occur in people with late-stage systemic sclerosis (SSc). Systemic sclerosis is a clinically diverse illness marked by intricate interactions between fibrosis, vasculopathy, and immunity. The skin, gastrointestinal tract, lungs, kidneys, and heart are among the organ systems that are impacted by this. Up to 60% of the mortality linked to SSc is caused by the two most prevalent pulmonary manifestations of the illness, interstitial lung disease and pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH).
ILD in patients with SSc is usually characterized by bilateral, ground-glass opacities, lower-lobe predominant reticulations, and occasionally honeycombing when seen on high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT). Because mild ILD patients may not exhibit any symptoms in the early stages of the illness, they might not have pulmonary function tests or diagnostic radiography done until they start to express symptoms like dyspnea upon exercise and a persistent cough. On late presentations of ILD, nothing is clear. Thus, the team led by Sabrina Hoa carried out this investigation to describe the incidence, risk factors, and consequences of late-onset SSc-ILD.
The participants without common ILD who were enrolled in the Canadian Scleroderma Research Group (CSRG) cohort between 2004 and 2020 were included. The HRCT was used to assess the incidence and risk variables for ILD based on the length of the illness, which was above (late) and below (early) 7 years from the first non-Raynaud presentation. Multivariable Cox models and Kaplan-Meier models were employed to compare the risk of ILD progression.
Incident ILD occurred in 199 patients (21%) of the total 969 patients over a median of 2.4 [1.2, 4.3] years. When compared to earlier SSc, the incidence rate in late SSc was lower. Male sex, myositis, diffuse subtype, anti-topoisomerase I autoantibodies, and elevated C-reactive protein levels were risk factors for incident ILD.
Arthritis and anti-RNA-polymerase III autoantibodies were more common in patients with late-onset ILD, and they were also less likely to be White. The degree of lung disease was comparable for SSc-ILD with late and early start. Also, the rates of progression for SSc-ILD with late and early onsets were comparable. Overall, the findings of this study support that ILD may manifest in in late SSc patients. The risk variables and rates of progression overlapped with earlier-onset SSc-ILD.
Source:
Hoa, S., Berger, C., Lahmek, N., Larche, M., Osman, M., Choi, M., Pope, J., Thorne, C., & Hudson, M. (2024). Characterisation of incident interstitial lung disease in late systemic sclerosis. In Arthritis & Rheumatology. Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.43051
Powered by WPeMatico

A recent retrospective cohort study published in the JAMA Ophthalmology highlighted the slow adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) systems for detecting diabetic retinopathy (DR) in the United States, despite their proven efficacy. The study analyzed the use of Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code 92229, established in January 2021 to support reimbursement for AI-based DR screening, across a database of over 107 million patients spanning 62 healthcare organizations.
The findings revealed that, out of nearly 5 million patients with diabetes examined from January 2019 to December 2023, only 4.2% underwent any ophthalmic imaging for DR. Within this subset, the use of AI-based imaging represented just 0.09% of total screenings, with only 3,440 patients utilizing the AI code 92229 since its inception. By 2023, the frequency of AI imaging had seen only a marginal increase, from 58.0 to 58.6 instances per 100,000 diabetic patients which indicated a slow adoption.
Also, traditional imaging techniques such as optical coherence tomography (OCT, CPT code 92134) and fundus photography (CPT code 92250) were more commonly used. OCT was performed in 80.3% of patients with at least one type of ophthalmic imaging, while fundus photography was utilized in 35.0% of cases. Traditional remote imaging (CPT codes 92227 and 92228) remained minimally used, accounting for only 1.0% and 2.5% of patients, respectively.
While the overall use of remote imaging methods surged by 90.16% between 2021 and 2023, AI-based screening remained disproportionately low. The data indicated that AI-based imaging had a higher referral rate to OCT (7.74%) when compared to traditional remote imaging (5.53%) by showing its potential for more targeted and effective DR detection. However, adoption hurdles such as cost, lack of awareness, and integration issues may be limiting widespread use. More than 80% of patients receiving AI-based imaging were concentrated in the South, a region comprising only 40% of other imaging modalities. Additionally, nearly half of the patients screened with AI systems were Black, in contrast to roughly a quarter seen in other imaging methods.
Despite FDA approval for AI-based systems like LumineticsCore and EyeArt, the broader implementation will require improved support for workflow integration and collaboration between primary care providers and ophthalmologists. The programs such as the Stanford Teleophthalmology Autonomous Testing and Universal Screening initiative highlight the importance of streamlined processes and patient-centered scheduling. Overall, the study points to a need for targeted strategies to boost the uptake of AI imaging, enhance early DR detection, and improve patient outcomes through more accessible and integrated screening solutions.
Source:
Shah, S. A., Sokol, J. T., Wai, K. M., Rahimy, E., Myung, D., Mruthyunjaya, P., & Parikh, R. (2024). Use of Artificial Intelligence–Based Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy in the US. In JAMA Ophthalmology. American Medical Association (AMA). https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2024.4493
Powered by WPeMatico

South Korea: A recent study published in Kidney Research and Clinical Practice has shed light on the impact of sacubitril-valsartan therapy on cardiac and kidney outcomes, particularly in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). The findings indicate that while patients experienced notable improvements in heart function, there was also a concerning decline in kidney function, raising important questions about the treatment’s dual effects.
“Patients with HFrEF who received sacubitril-valsartan showed notable enhancements in cardiovascular outcomes, even in the presence of acute kidney injury (AKI)” the researchers wrote.
Sacubitril-valsartan, a combination medication designed to enhance cardiac function and reduce cardiovascular mortality by inhibiting neprilysin and blocking angiotensin II receptors, has emerged as a pivotal therapy for HFrEF. However, the long-term protective effects of sacubitril-valsartan on cardiac function in the presence of concurrent AKI are still uncertain. To fill this knowledge gap, Hyo Jeong Kim, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea, and colleagues examined the relationship between the recovery of cardiac function and the decline in kidney function.
For this purpose, the researchers enrolled 512 patients with HFrEF who began treatment with either sacubitril-valsartan or valsartan in cohort 1. They also included patients from cohort 2 who experienced acute kidney injury (AKI) and underwent follow-up transthoracic echocardiography. In cohort 1, the analysis focused on short- and long-term kidney outcomes. For cohort 2, the researchers examined changes in cardiac function with changes in kidney function following the initiation of the medication.
The study revealed the following findings:
The study demonstrated that the decline in kidney function with sacubitril-valsartan was comparable to that seen with valsartan. Among patients who experienced acute kidney injury, those on sacubitril-valsartan showed greater improvements in cardiovascular health than those on valsartan.
“These findings offer valuable insights for managing patients with HFrEF and underscore the complexities involved in addressing both heart failure and kidney function,” the researchers concluded.
Reference:
Kim, Hyo Jeong, et al. “Cardiac and Kidney Outcomes After Sacubitril-valsartan Therapy: Recovery of Cardiac Function Relative to Kidney Function Decline.” Kidney Research and Clinical Practice, vol. 43, no. 5, 2024, pp. 614-625.
Powered by WPeMatico
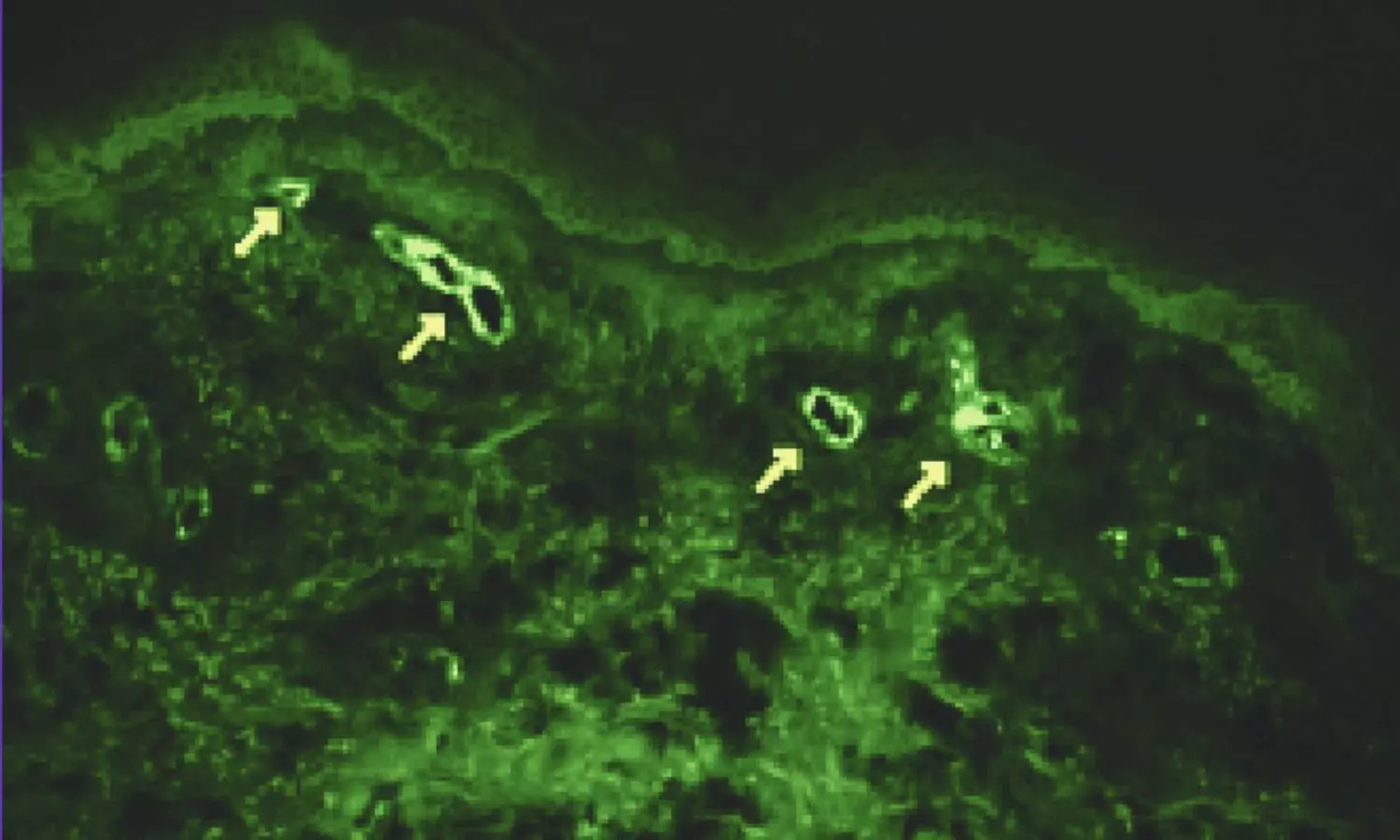
USA: A recent scoping review has highlighted the diagnostic utility of direct immunofluorescence (DIF) test panels in assessing cutaneous vasculitis, a group of disorders characterized by inflammation of blood vessels in the skin.
The review, published in the Journal of Cutaneous Pathology emphasizes that DIF testing plays a crucial role not only in confirming a diagnosis of vasculitis but also in classifying disease subtypes and predicting potential systemic associations.
Cutaneous vasculitis can manifest in various ways, leading to skin lesions that may mimic other dermatological conditions. Accurate diagnosis is vital, as the treatment and management of vasculitis can differ significantly from other skin disorders.
Given the immune-mediated nature of non-infectious cutaneous vasculitis, skin biopsy samples are frequently sent for DIF testing when vasculitis is suspected clinically. However, the clinical significance of DIF testing has not been thoroughly evaluated in the existing literature. To fill this knowledge gap, Julia S Lehman, Department of Dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA, and colleagues systematically assessed the peer-reviewed literature on the utility of DIF in vasculitis to help inform the development of appropriate use criteria by the American Society of Dermatopathology.
For this purpose, the researchers searched two electronic databases for articles on direct immunofluorescence (DIF) and vasculitis, covering the period from January 1975 to October 2023. They included relevant case series featuring three or more patients, published in English, and available in full text. Additional articles were identified through manual reference review. Given the heterogeneity of the studies, the findings were analyzed descriptively.
The key findings were as follows:
“The use of DIF testing, along with biopsy and hematoxylin and eosin staining, continues to be a cornerstone of the gold standard work-up for diagnosing vasculitis. This is particularly true for IgA vasculitis, where IgA deposits are closely linked to an increased risk of renal disease,” the researchers wrote.
“Further studies are needed to compare the sensitivity of DIF testing with that of histopathology,” they concluded.
Reference:
Lehman JS, Ferringer TC, Fung MA, Cassarino DS, Shalin SC. Diagnostic utility of direct immunofluorescence test panels for cutaneous vasculitis: A scoping review. J Cutan Pathol. 2024 Sep 22. doi: 10.1111/cup.14722. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 39307568.
Powered by WPeMatico

A recent study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research found that combining dexamethasone and vitamin B12 (VB12) through epidural injection can significantly improve early postoperative outcomes for patients undergoing percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy (PEID).
PEID is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat lumbar disc herniation (LDH). While it is generally effective, some patients experience residual pain post-surgery, impacting their recovery and overall quality of life. The study investigated whether supplementing PEID with epidural injections of dexamethasone and VB12 could reduce postoperative pain and improve recovery metrics.
This study enrolled patients who had undergone PEID for LDH and randomly divided them into 2 groups where one was the single surgery (SS) group, which only received PEID and the other was combined treatment (CT) group, which received both the surgery and an epidural injection of dexamethasone and VB12. The evaluation criteria included the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) for pain, the Japanese Orthopaedic Association (JOA) score for functional assessment, and the Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) for measuring disability. Other important metrics included the expression levels of serum inflammatory factors, adverse surgical events, postoperative hospitalization duration, and overall recovery according to the modified MacNab criteria.
The results indicated that patients in the CT group experienced significantly lower VAS scores for low back and leg pain at 1, 3, and 7 days post-surgery when compared to the SS group (P < 0.05). Also, 7 days after surgery, JOA and ODI scores reflected greater improvements in the CT group by underlining improved functional recovery and reduced disability (P < 0.05). Although there were no significant differences at other time points, early postoperative pain management was notably better in the CT group.
Serum analysis revealed that inflammatory markers were lower in the CT group 3 days after surgery by suggesting that the combined treatment played a role in moderating the inflammatory response (P < 0.05). This may contribute to the reported reductions in pain and shorter hospital stays for patients in the CT group (P < 0.05).Both groups had a high rate of positive outcomes, with 89.3% in the SS group and 92.2% in the CT group achieving favorable recovery (P = 0.945) which indicated the overall safety of the combined treatment. Overall, the addition of dexamethasone and VB12 via epidural injection can effectively reduce early postoperative pain, reduce inflammation, and improve initial recovery after PEID.
Reference:
He, C., Li, J., Hu, W., Xiao, B., Fan, T., Zhou, J., Shuang, F., & Li, H. (2024). Effects of dexamethasone combined with vitamin B12 on percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy early outcomes: a randomized controlled trial. In Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (Vol. 19, Issue 1). Springer Science and Business Media LLC. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-024-05210-z
Powered by WPeMatico

Recently the U.S. Food and Drug
Administration (FDA) issued updated safety warnings for all glucagon-like
peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) about the risk of pulmonary aspiration
during procedures that require general anesthesia or deep sedation. The updated
news was published in the ‘Drug Safety-related Labeling Changes’ portal of the
U.S.F.D.A website.
The medications whose safety labeling
was updated include semaglutide (Ozempic, Rybelsus, Wegovy); liraglutide
(Saxenda, Victoza); and the dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide
(GIP)/GLP-1 tirzepatide (Mounjaro, Zepbound). The updated product labeling
included “Warnings and Precautions,” as a new subsection. This change was done
as there were rare postmarketing reports of pulmonary aspiration among patients
taking GLP-1 RAs who underwent elective surgeries or procedures requiring
general anesthesia or deep sedation.
Despite the patients following
the preoperative fasting guidelines, some of these unfortunate incidents were reported.
There is insufficient data to provide specific recommendations on vindicating
this risk as per the FDA. There is uncertainty on whether adjusting
preoperative fasting protocols or temporarily stopping GLP-1 RA treatment could
reduce the retained gastric contents and the aspiration. Evidence suggests that
GLP-1 RAs may cause delayed gastric emptying, leading to the presence of
residual stomach contents even after recommended fasting periods. This slower
gastric motility increases the risk of complications during anesthesia, as
residual contents can inadvertently enter the lungs (aspiration) when patients
are under deep sedation or anesthesia.
To mitigate the risk of pulmonary
aspiration, patients are now advised to inform their healthcare providers if
they take any GLP-1 RAs before scheduling surgery or anesthesia procedures. In
addition to this, the new warning was also added to the “Adverse Reactions” and
“Postmarketing Experience” sections of the drug labels to recognize pulmonary
aspiration linked to GLP-1 RAs during surgeries requiring anesthesia.
The information in the medication
guide section of the drug labels has also been updated and patients are also instructed
to inform the healthcare providers, especially anesthesiologists and surgeons,
about their use of GLP-1 RAs before undergoing any surgical procedures.
Responsibility has also been
levied on the Healthcare providers to advise and counsel the patient’s risk
associated with GLP-1 RAs. Information about the delaying of stomach emptying, and
risks during surgery or procedures involving anesthesia should be given before
prescribing these medications. So that the patients can in turn inform the healthcare
providers before undergoing any procedures.
Powered by WPeMatico
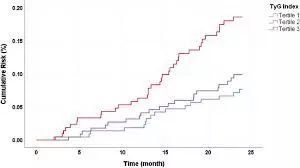
Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue BanA study published in the Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban suggests that elevated levels of TyG and TyG-obesity composite indices were associated with a higher risk for IHD.
A study was done to explore the association between the triglyceride-glucose index (TyG) and TyG-obesity composite indices, including TyG-waist circumference (TyG-WC), TyG-body mass index (TyG-BMI), and TyG-waist-to-height ratio (TyG-WHtR), and the risk of ischemic heart disease (IHD), and to provide reference for the prevention of IHD. The sample of this study was derived from the West China Elderly Preventive and Treatment Merging Cohort, from which 9628 elderly individuals from the retrospective cohort were selected. Cox regression models were used to analyze the association between TyG-related indices and the risk of IHD. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were plotted to assess and compare the performance of TyG-related indices in predicting the occurrence of IHD. Results: The participants were followed up for a median of 2.82 years, with 7.2% (694/9628) of the participants experiencing IHD events. Multivariate Cox regression showed that after controlling for the covariates, including sex, age, educational attainment, smoking, drinking, exercise, dietary habits, medication history, and whether the participant had hypertension, every time TyG, TyG-WC, TyG-BMI and TyG-WHtR increased by one standard deviation (SD), the risk of IHD increased by 12% (hazard ratio [HR]=1.12, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.04-1.20), 21% (HR=1.21, 95% CI: 1.12-1.31), 20% (HR=1.20, 95% CI: 1.12-1.29), and 19% (HR=1.19, 95% CI: 1.10-1.28), respectively. Both the TyG index and TyG-obesity composite indices were positively correlated with IHD risk, showing a linear relationship (P<0.05). TyG-WC (area under the curve[AUC]=0.680, 95% CI: 0.660-0.700, P<0.001), TyG-BMI (AUC=0.674, 95% CI: 0.654-0.695, P<0.001), and TyG-WHtR (AUC=0.678, 95% CI: 0.658-0.698, P<0.001) demonstrated better predictive performance than TyG did (AUC=0.669, 95% CI: 0.648-0.689, P<0.001). Elevated levels of TyG and TyG-obesity composite indices were associated with a higher risk for IHD, and combining TyG with BMI, WC, and WHtR may lead to better performance in risk assessment for IHD than using TyG alone.
Reference:
Yang, Jing, et al. “[Association Between Triglyceride Glucose Index and Triglyceride Glucose-Obesity Composite Indices and the Risk of Ischemic Heart Disease].” Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao. Yi Xue Ban = Journal of Sichuan University. Medical Science Edition, vol. 55, no. 5, 2024, pp. 1123-1132.
Keywords:
Elevated, levels, TyG, TyG, -obesity, composite, indices, associated, highe, risk, IHD, Study, Yang, Jing, Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban
Powered by WPeMatico
