Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana achieves target of Rs 1000 crore in sales in FY 2023-24
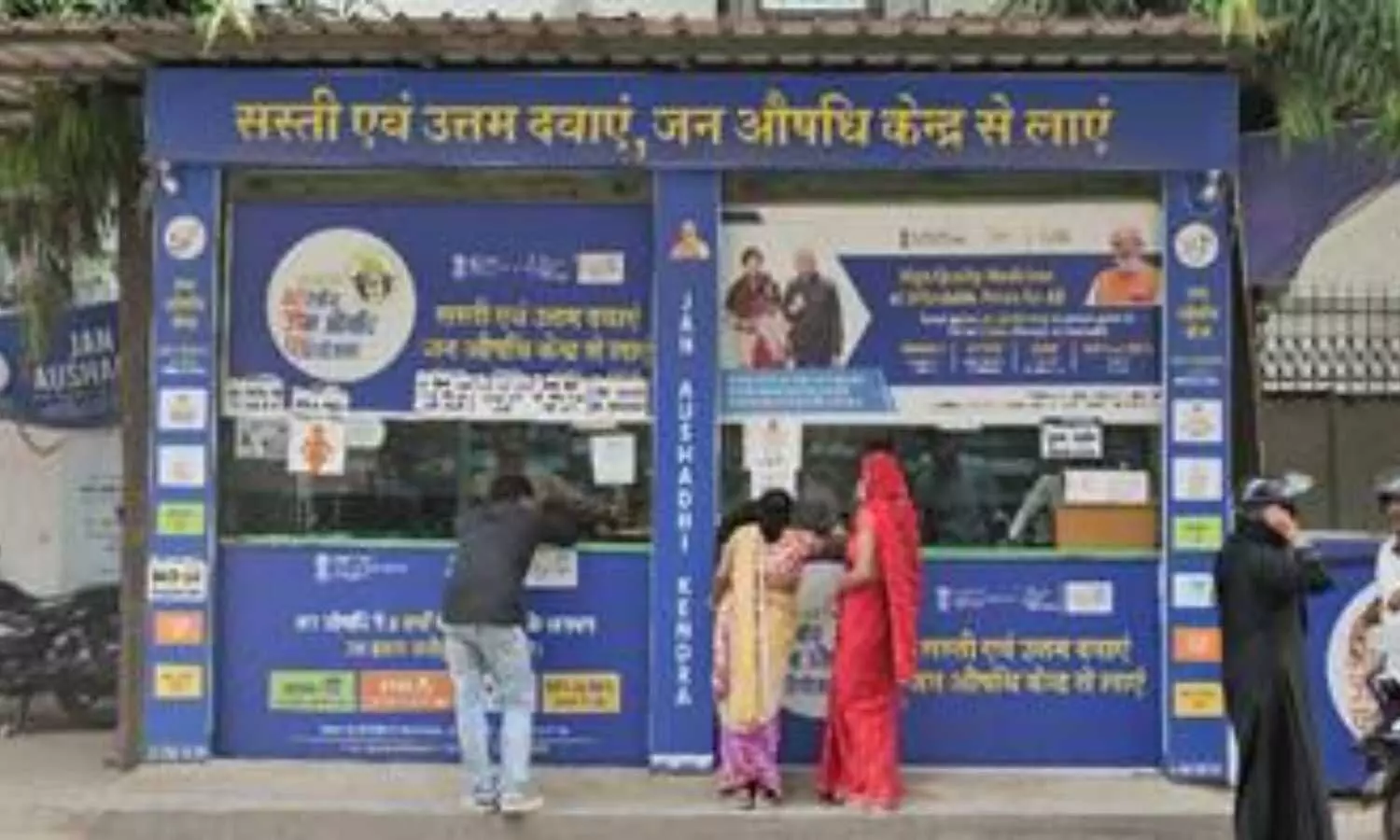

New Delhi: Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana (PMBJP) has created another landmark in the history of generic medicines in the country by selling medicines worth Rs. 1000 Crore this year. This achievement was made possible only by the people of the country, who have saved approximately 5000 crores by purchasing medicines from Jan Aushadhi Kendras which is present in more than 785 districts of the country. This substantial growth is a testament to PMBI’s commitment to serving more communities and reaching a broader audience.
In last 9 years, there has been more than 100 times growth in number of Kendras which were only 80 in 2014 and have now grown to almost 10000 Kendras covering almost all the districts of the country. Hon’ble Prime Minister in his Independence Day speech, 2023 has announced for opening of 25,000 Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Kendras (PMBJKs) across the country.
The Prime Minister virtually launched the 10,000th Janaushadhi Kendra at AIIMS, Deoghar, Jharkhand on 30th November, 2023 and further paved the way for expanding the number of Kendras to 25,000 for wider outreach and easy accessibility of medicines to the people of the country.
Accordingly, the Government has set a target to open 25,000 Janaushadhi Kendras across the country by March, 2026. Keeping up the promise, online applications have been called for opening of new Janaushadhi Kendras across all districts of the nation through the official website of PMBI.
Under this scheme, there are more than 10,000 functional Janaushadhi Kendras across the country. The product basket of PMBJP comprises 1963 medicines and 293 surgical devices covering all major therapeutic groups such as Cardiovascular, Anti-cancers, Anit-diabetics, Anti-infectives, Anti-allergic, Gastro-intestinal medicines, Nutraceuticals, etc. There are five warehouses at Gurugram, Bengaluru, Chennai, Guwahati and Surat. These are backed by SAP based inventory management system. Further, 36 distributors are functional across the country to support the supply of medicines to remote and rural areas. PMBJP has further added number of Ayurvedic products in its product basket for immunity boosting and it is easily available at affordable prices for people.
Read also: Jan Aushadhi scheme has led to savings of Rs 7416 cr for citizens this fiscal: Govt
Powered by WPeMatico