CPC plus CHX mouthwash fails to reduce COVID-19 viral load of saliva

Preprocedural rinsing with cetylpyridinium chloride plus chlorhexidine mouthwash fails to reduce COVID-19 viral load of saliva suggests a new study published in the of Clinical Periodontology.
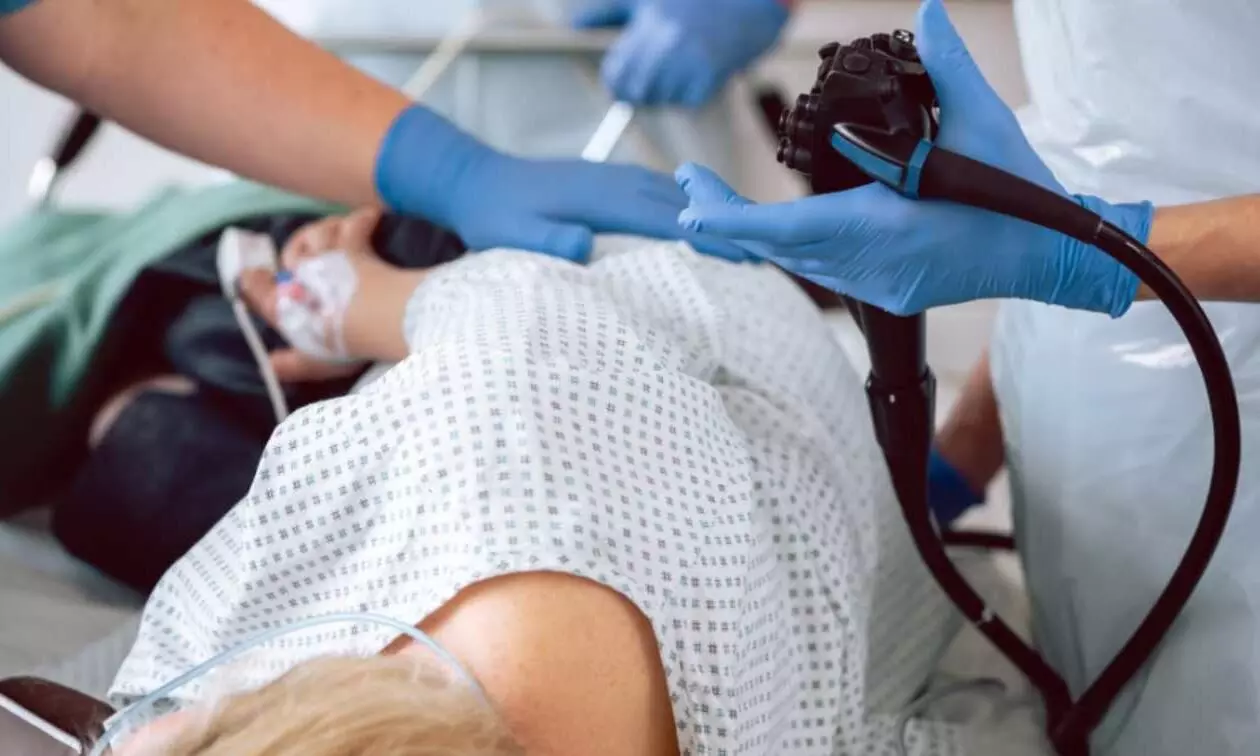
This study aimed to investigate the efficacy of a 0.05% cetylpyridinium chloride–0.05% chlorhexidine (CPC–CHX) mouthwash in reducing viral load in the saliva as compared with sterile water. Forty SARS-CoV-2 positive patients were asked to dispense 4 mL of saliva. Half the patients rinsed for 60 s with 15 mL CPC–CHX, and the remaining patients rinsed with sterile water (control). Four millilitres of saliva were collected after 15, 30 and 60 min after rinsing. Quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) specific for SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein were performed. For ELISA, the intact (representing the active virus) to total virus load (I/T) was calculated.Results: SARS-CoV-2 copy numbers/mL from RT-qPCR tended to decrease in the control group, whereas in the CPC–CHX group, an increase was observed after T30. However, mixed linear model analysis revealed no statistical differences between groups (p = .124), time points (p = .616) and vaccinated or non-vaccinated patients (p = .953). Similarly, no impact of group (p = .880), time points (p = .306) and vaccination (p = .711) was observed for I/T ratio values. Within the limitation of this study, there was no evidence that the intervention reduced salivary SARS-CoV-2 viral load during the course of 60 min. Therefore, commonly used pre-procedural rinsing might not be clinically relevant.
Reference: Giulia, B., Viktoria, W., Robert, K., Michael, B., Nadine, L., Jürgen, B., Beryl, S.-H., Jörg, T., & Kathrin, B. (2023). Eligibility and efficacy of a CPC- and CHX-based antiviral mouthwash for the elimination of SARS-CoV-2 from the saliva: A randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical trial. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.13905
Keywords: Preprocedural, rinsing, with, cetylpyridinium, chloride, plus, chlorhexidine, mouthwash, fails, to, reduce, COVID-19, viral load, saliva, Journal of Clinical Periodontology, Giulia, B., Viktoria, W., Robert, K., Michael, B., Nadine, L., Jürgen, B., Beryl, S.-H., Jörg, T., & Kathrin, B
Powered by WPeMatico