RFK Jr. is wrong about mRNA vaccines: A scientist explains how they make COVID less deadly
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
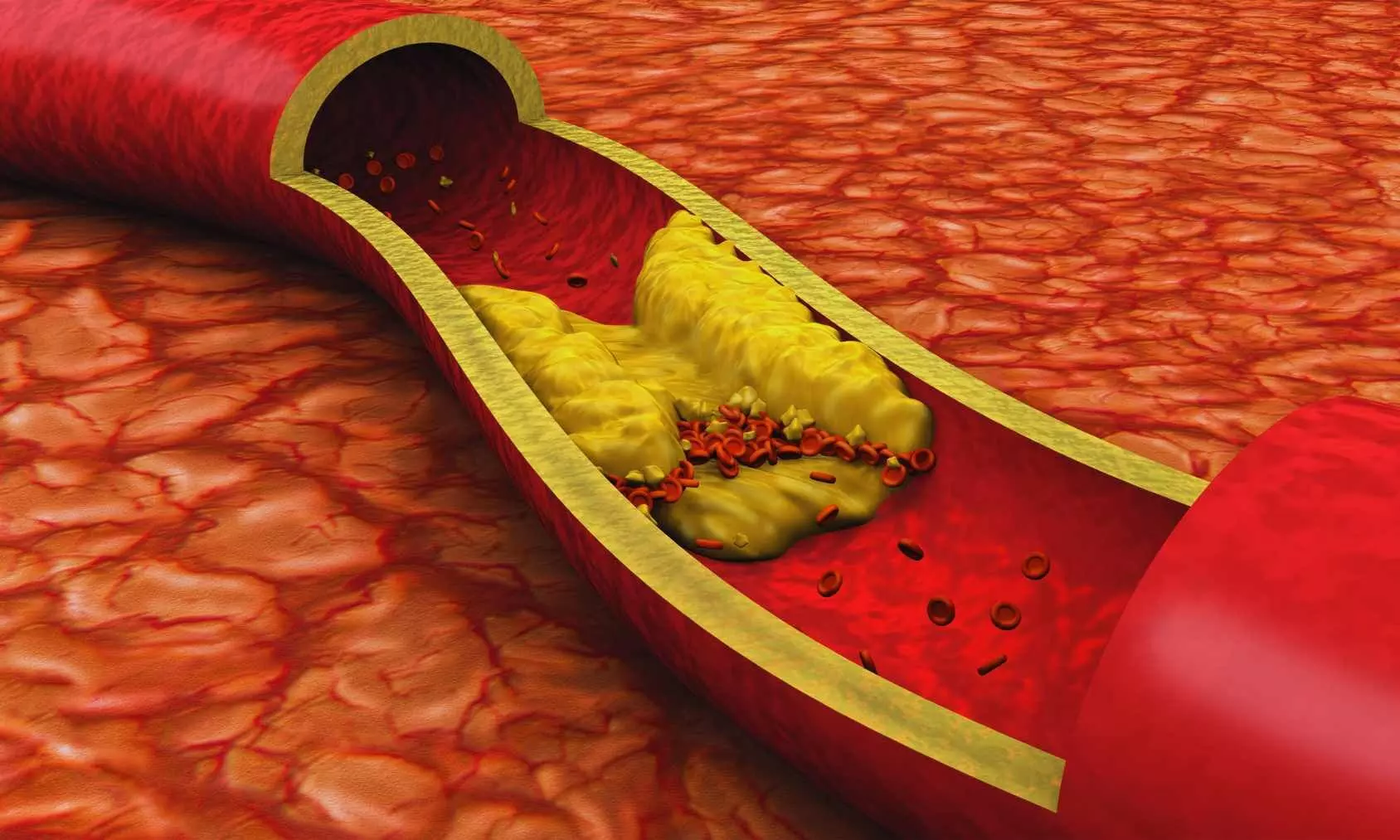
The FDA has approved inclisiran (Leqvio) for first-line use in lowering LDL cholesterol, even without combining it with statins, according to Novartis.
The FDA proactively requested the label update based on the robust LDL-C lowering data for PCSK9-targeting therapies.
“This first-line label update reinforces Leqvio’s proven ability to effectively lower LDL-C, a critical risk factor for heart disease,” said Victor Bultó, President, US, Novartis. “With this new indication enabling Leqvio’s use as monotherapy along with diet and exercise, we now have the potential to help even more patients achieve their LDL-C lowering goals earlier in their treatment journey.”
With its twice-yearly, health care provider-administered dosing, Leqvio is uniquely positioned to help support patient adherence and long-term LDL-C management, including goal attainment. This is a critical unmet need, as up to 80% of ASCVD patients in the US struggle to reach the LDL-C guideline-recommended target of <70 mg/dL. This need is heightened by the latest 2025 ACC/AHA Joint Committee Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes, which recommends more aggressive treatment to achieve LDL-C targets.
The updated label removes the requirement for Leqvio to be used on top of or in combination with statin therapy. Other updates include revising “primary hyperlipidemia” to the more specific term of “hypercholesterolemia” throughout the label, to more accurately focus on LDL-C reduction.
After an initial dose and another at three months.
Leqvio is an injectable prescription medicine indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in adults with hypercholesterolemia, including heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH).
Novartis has obtained global rights to develop, manufacture and commercialize Leqvio under a license and collaboration agreement with Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, a leader in RNAi therapeutics.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) affects hundreds of millions of people and claims more lives globally than cancer, chronic lung disease and diabetes combined. Around 80% of premature cardiovascular deaths can be prevented by addressing factors that cause or worsen CVD.
ASCVD accounts for 85% of all CV deaths. Its burden in the US is greater than that of any other chronic diseases. ASCVD is caused by the development and growth of plaques in the inner lining of the arteries. The atherosclerotic plaque is mainly composed of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) that accumulates over time. Cumulative exposure to LDL-C can increase one’s risk of cardiovascular events such as a heart attack or stroke.
Powered by WPeMatico
Although metformin has been the go-to medication to manage type 2 diabetes for more than 60 years, researchers still do not have a complete picture of how it works. Scientists at Baylor College of Medicine and international collaborators have discovered a previously unrecognized new player mediating clinically relevant effects of metformin: the brain. By uncovering a brain pathway involved in metformin’s anti-diabetic action, researchers have discovered new possibilities for treating diabetes more effectively and precisely. The study appeared in Science Advances.
“It’s been widely accepted that metformin lowers blood glucose primarily by reducing glucose output in the liver. Other studies have found that it acts through the gut,” said corresponding author Dr. Makoto Fukuda, associate professor of pediatrics – nutrition at Baylor. “We looked into the brain as it is widely recognized as a key regulator of whole-body glucose metabolism. We investigated whether and how the brain contributes to the anti-diabetic effects of metformin.”
The team focused on a small protein called Rap1, found in a specific part of the brain known as the ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH). The researchers discovered that metformin’s ability to lower blood sugar at clinically relevant doses depends on turning off Rap1 in this brain region.
To test this, the Fukuda lab and his colleagues used genetically modified mice that lacked Rap1 in their VMH. These mice were fed a high-fat diet to mimic type 2 diabetes. When given low doses of metformin, the drug failed to lower their blood sugar. However, other diabetes medications like insulin and GLP-1 agonists still worked.
To further show that the brain is a key player, the researchers injected tiny amounts of metformin directly into the brains of diabetic mice. The result was a significant drop in blood sugar, even with doses thousands of times smaller than what’s typically given by mouth.
“We also investigated which cells in the VMH were involved in mediating metformin’s effects,” Fukuda said. “We found that SF1 neurons are activated when metformin is introduced into the brain, suggesting they’re directly involved in the drug’s action.”
Using brain slices, the scientists recorded the electrical activity of these neurons. Metformin made most of them more active, but only if Rap1 was present. In mice lacking Rap1 in these neurons, metformin had no effect, showing that Rap1 is essential for metformin to “switch on” these brain cells and lower blood sugar.
“This discovery changes how we think about metformin,” Fukuda said. “It’s not just working in the liver or the gut, it’s also acting in the brain. We found that while the liver and intestines need high concentrations of the drug to respond, the brain reacts to much lower levels.”
Although few anti-diabetic drugs act on the brain, this study shows that widely used metformin has been doing so all along. “These findings open the door to developing new diabetes treatments that directly target this pathway in the brain,” Fukuda said. “In addition, metformin is known for other health benefits, such as slowing brain aging. We plan to investigate whether this same brain Rap1 signaling is responsible for other well-documented effects of the drug on the brain.”
Reference:
Hsiao-Yun Lin et al. ,Low-dose metformin requires brain Rap1 for its antidiabetic action.Sci. Adv.11,eadu3700(2025).DOI:10.1126/sciadv.adu3700
Powered by WPeMatico

A new study published in the Journal of American Heart Association revealed that clusters of cardiovascular risk factors during pregnancy markedly increased the probability of stillbirth.
It is often acknowledged that stillbirth, which is the intrauterine death of a fetus that usually happens between 20 and 28 weeks of gestation, is a crucial sign of the calibre and efficacy of health care systems throughout pregnancy and childbirth. It has been determined that one modifiable and controllable risk factor for stillbirth is the cardiovascular health of the mother before to pregnancy.
It is still unclear how certain clusters of prenatal cardiovascular risk factors relate to stillbirth, especially when it comes to different racial and ethnic groupings. With a focus on racial inequities, this study sought to assess the relationship between stillbirth and 16 different cardiovascular risk groups.
Using the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Natality and Fetal Death Data Files (2014–2022), researchers carried out a population-based analysis across the country that included 131,047 stillbirths (defined as births that occurred at least 20 weeks gestation) and 31,408,776 singleton births. 16 mutually incompatible clusters were created using the prepregnancy cardiovascular risk factors (smoking, hypertension, diabetes, and nonideal body mass index).
Pregnancy diabetes posed the highest risk, followed by prepregnancy hypertension (95% CI, 2.27–2.63), smoking (95% CI, 1.58–1.67), and unhealthy body mass index (95% CI, 1.31–1.35). These findings were obtained from the analysis of 16 groups defined by the four binary risk factors. 2 out of 6 risk combinations, mostly those involving diabetes, showed the absolute extra risk related to the biological interaction between 2 risk variables.
There were clear racial differences, with non-Hispanic Black women having the highest absolute and relative odds of stillbirth-nearly twice as high as non-Hispanic White mothers.
Overall, this study demonstrated a substantial correlation between the risk of stillbirth, specific risk clusters, and prepregnancy cardiovascular risk factor scores. This research created 16 different risk clusters by combining four binary risk variables, and they discovered that the relationships between these clusters with stillbirth varied, with some single risk factors (where no other factors were present) exhibiting larger connections.
Source:
Nie, J., Rezende, L. F. M., Ferrari, G., Qiu, Y., Wang, X., Huang, W., Niu, Z., Chen, X., & Aune, D. (2025). Association of prepregnancy cardiovascular risk factors clusters with stillbirth risk across racial and ethnic groups: A nationwide population-based study of 31.4 million singleton births and 131 047 stillbirths. Journal of the American Heart Association. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.124.042319
Powered by WPeMatico

New Delhi: With an aim to demonstrate the safety and efficacy on lower back pain, the Subject Expert Committee (SEC) functioning under the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) has opined that Elevate Scientific should conduct the clinical investigation of Radiopaque Gelified Ethanol (Absolute Gel) on the Indian population.
In addition, the expert panel suggested that the firm needs to submit the Clinical Investigation Protocol with a statistically significant sample size for taking further necessary action in the matter.
This came as Elevate Scientific presented clinical study data generated globally (Iran, Italy, etc.) along with post-marketing data on Radiopaque Gelified Ethanol (Absolute Gel) for the waiver of one of the conditions of the permission for manufacturing obtained under Form MD27 and proposed to allow them to market the product for domestic use.
Radiopaque gelified ethanol, also known as Absolute Gel, is a minimally invasive treatment for disc herniations using a substance injected into the disc under imaging guidance. It’s a gelified ethanol solution with tungsten particles, designed to be more viscous than pure ethanol and to allow for tracking during the procedure. The gel, upon contact with the nucleus pulposus, dehydrates it, leading to a retraction of the herniated disc and potential pain relief.
At the recent SEC meeting for analgesic and rheumatology (Medical Devices Division) held on 16th July 2025, the expert panel reviewed the clinical study data generated globally (Iran, Italy, etc.) along with post-marketing data on radiopaque gelified ethanol (absolute gel) presented by Elevate Scientific for the waiver of one of the conditions of the permission for manufacturing obtained under Form MD27.
After detailed deliberation, the committee observed that the clinical study data presented by the firm does not demonstrate the safety and efficacy of pain outcomes of the patients.
Therefore, the committee recommended that the firm should conduct the clinical investigation on the Indian population with the objective of demonstrating the safety and efficacy on lower back pain.
In accordance with the above, the expert panel stated that the firm needs to submit the Clinical Investigation Protocol with a statistically significant sample size for taking further necessary action in the matter.
Powered by WPeMatico

New Delhi: Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Limited has received approval from the Subject Expert Committee (SEC) under CDSCO to conduct a Phase III clinical trial of its investigational dermatological product Tapinarof Cream 1%, aimed at treating plaque psoriasis.
The decision was made during the SEC’s 7th meeting held on 23rd July 2025 at CDSCO headquarters, New Delhi, where the firm presented its proposal for the grant of permission to manufacture and market the drug, along with the full Phase III clinical trial protocol.
The proposed trial is titled:
“A randomized, multi-center, double-blind, parallel group, three-arm, placebo-controlled trial to evaluate the clinical equivalence of Tapinarof cream 1% of Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd versus VTAMA® (Tapinarof cream 1%, Dermavant Sciences Inc.) using the clinical endpoint in patients with plaque psoriasis”.
The study will be conducted under protocol number DRL-IND-NDA30-TAP/2024, version 3.0 dated 17.04.2025. It is designed to evaluate the clinical equivalence of Dr. Reddy’s Tapinarof formulation to the reference product VTAMA®, already approved internationally and marketed by Dermavant Sciences Inc.
Tapinarof is an aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) agonist, a novel non-steroidal topical treatment for plaque psoriasis. Its mechanism involves modulating immune responses and skin barrier repair, offering a potential steroid-free alternative for patients with chronic skin conditions.
After reviewing the clinical protocol and related materials, and following detailed deliberation, the SEC found the submitted plan appropriate and aligned with regulatory expectations for comparative efficacy and safety evaluation.
“After detailed deliberation, the committee recommended for grant of permission to conduct Phase III clinical trial of drug Tapinarof Cream 1% as per protocol presented by the firm.”
Powered by WPeMatico
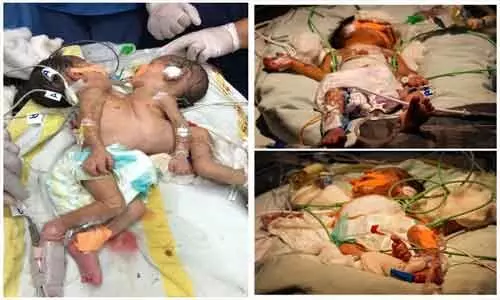
Twin reversed arterial perfusion (TRAP) sequence is a rare and serious complication primarily observed in monochorionic monoamniotic (MCMA) twins, manifesting with acute impacts on both twins involved. With a historically low incidence of approximately 1%, the advent of advanced ultrasonography and assisted reproductive technologies may increase the observed frequency, potentially up to 1 in 40 MC twin pregnancies. Notably, about 30% of cases emerge specifically in MCMA gestations, while conjoined twins, a rare subtype of monochorionic twins, present an even lower incidence. TRAP sequence’s defining characteristic is the dependency of the acardiac twin on the cardiac output of the pump twin, facilitated through unique vascular connections typically identifiable via prenatal ultrasound. A recent investigation showcases an unusual instance of the TRAP sequence linked to conjoined twins, where the acardiac twin was supplied with blood through a direct branch originating from the aortic arch of the pump twin.
Mortality and Management Strategies
The condition exhibits alarmingly high mortality rates, with spontaneous miscarriage rates reaching 35-50% and the risk of pump twin mortality estimated at 30% by 18 weeks gestation without intervention. Effective management strategies aim to prolong gestation and circumvent severe complications, such as fetal hydrops and heart failure. Common interventions comprise expectant monitoring, radiofrequency ablation (RFA), and laser coagulation, with RFA gaining favor due to its minimally invasive nature and potential for improved outcomes. The optimal window for intervention remains under investigation, generally advocated at 14-18 weeks of gestation, although recent insights suggest the potential advantages of even earlier intervention.
Case Study and Intervention Outcomes
A case studied illustrated a unique variation in TRAP sequence wherein the acardiac twin was perfused through a direct branch from the pump twin’s aortic arch. Utilizing RFA effectively occluded this abnormal blood supply, leading to a successful pregnancy outcome. Post-procedure evaluations demonstrated stable hemodynamics in the pump twin post-ablation, allowing for a healthy delivery at 35 weeks with a normal birth weight and Apgar score, reinforcing the utility of timely intervention and the importance of multidisciplinary collaboration throughout management.
Evaluation of Treatment Efficacy
Subsequent evaluations indicated significant regression in size of the acardiac twin following intervention, underscoring the benefits of individualized treatment strategies. Furthermore, systematic reviews support a marked improvement in survival rates through timely interventions, particularly with RFA. Despite limitations such as a small sample size and the absence of late-gestation fetal brain MRI assessments, the findings present valuable insights into the importance of early diagnostics and a tailored approach for improved outcomes in high-risk pregnancies, advocating for future studies integrating larger datasets and machine learning techniques for enhanced decision-making.
Key Points
– -Incidence and Classification-: TRAP sequence predominantly occurs in monochorionic monoamniotic (MCMA) twin pregnancies, with an estimated incidence of approximately 1%, which may increase to 1 in 40 due to advancements in ultrasound and reproductive technologies. About 30% of cases occur within MCMA gestations, while conjoined twins represent a rarer variant.
– -Pathophysiology-: The defining feature of TRAP sequence is the reliance of the acardiac twin on the pump twin’s cardiac output through anomalous vascular connections, typically visualized via prenatal ultrasound.
– -Mortality Rates-: TRAP sequence is associated with high mortality rates, exhibiting a spontaneous miscarriage rate of 35-50% and a 30% risk of mortality for the pump twin by 18 weeks gestation in the absence of intervention.
– -Management Strategies-: Treatment focuses on prolonging gestation and avoiding complications like fetal hydrops and heart failure. Effective interventions include expectant management, radiofrequency ablation (RFA), and laser coagulation, with RFA being preferable due to its minimally invasive nature. The optimal intervention window is generally recommended between 14-18 weeks, though earlier intervention may be beneficial.
– -Case Study Outcomes-: A case study exemplified a variation where the acardiac twin was perfused via a directly connected branch from the pump twin’s aorta. The application of RFA successfully occluded this supply, leading to positive hemodynamic stability for the pump twin, resulting in delivery at 35 weeks with normal birth metrics, emphasizing the need for timely and collaborative intervention.
– -Efficacy and Future Directions-: Post-intervention assessments showed significant reduction in the size of the acardiac twin, indicating the effectiveness of tailored treatment. Systematic reviews highlight improved survival rates with timely interventions like RFA, though limitations exist regarding sample sizes and imaging assessments. Future research should expand datasets and incorporate machine learning methods to refine clinical decision-making in these complex scenarios.
Reference –
Hua Lai et al. (2025). Individualized Intervention And Growth Dynamics Assessment In TRAP Sequence With Conjoined Twins Based On Radiofrequency Ablation. *BMC Pregnancy And Childbirth*, 25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-025-07658-1.
Powered by WPeMatico
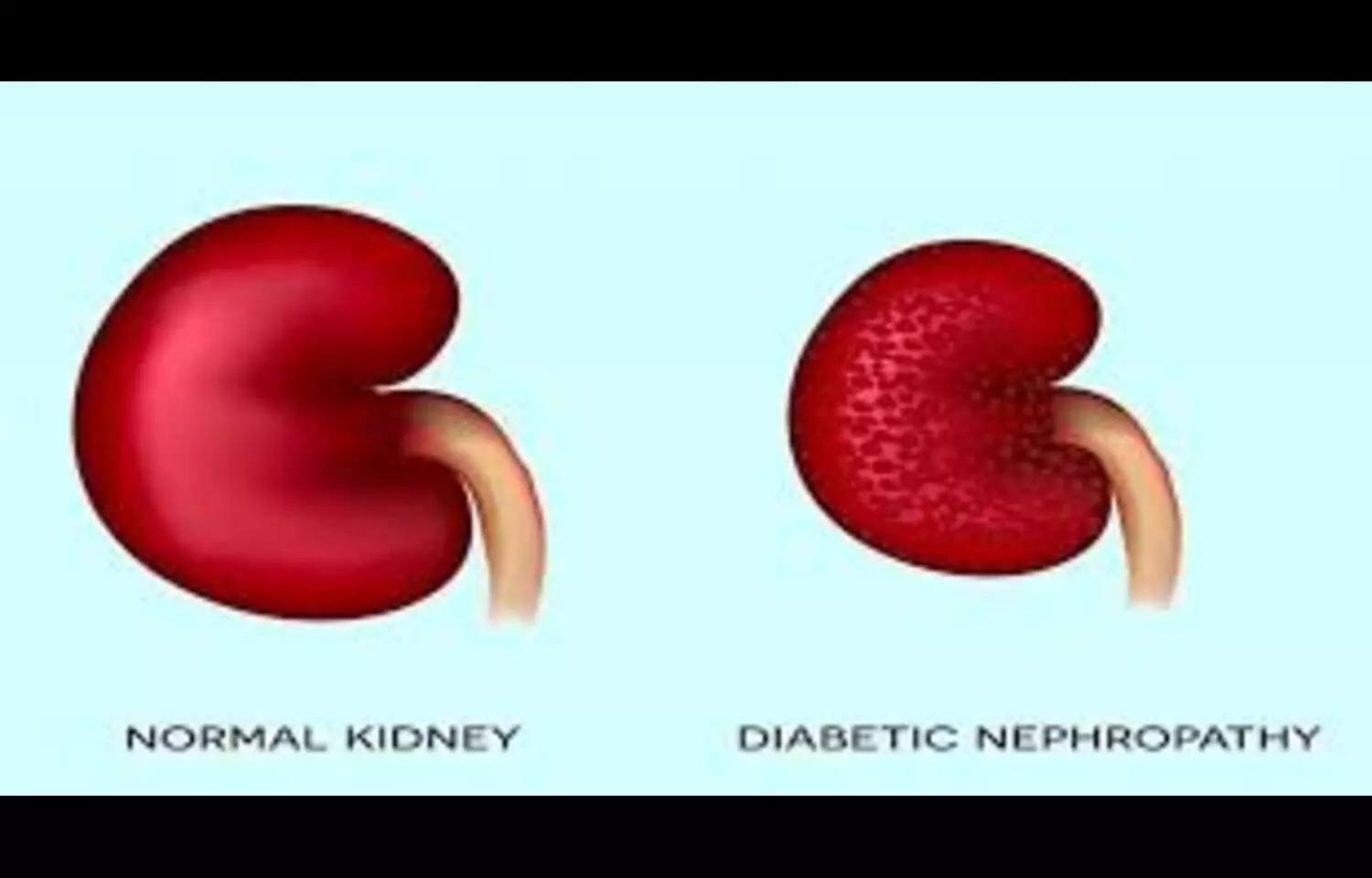
A new study published in BMC Nephrology has found that elevated levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) are significantly associated with an increased risk of diabetic nephropathy (DN), a serious microvascular complication of diabetes. Researchers analyzed data across multiple studies and concluded that hs-CRP—an inflammatory biomarker—may serve as a useful tool for identifying high-risk individuals and informing targeted anti-inflammatory treatment strategies. The findings point to the role of systemic inflammation in the pathogenesis of diabetic kidney disease, suggesting that hs-CRP could be integrated into risk stratification models alongside traditional markers like albuminuria and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Despite these insights, the authors note that considerable heterogeneity among included studies—such as differences in diagnostic criteria, populations, and study design—limits the generalizability of the results. Therefore, while the data is promising, further prospective and mechanistic studies are required to confirm causality and refine clinical application. This research contributes to growing evidence that chronic low-grade inflammation plays a central role in diabetic complications, and highlights hs-CRP as a potentially accessible, low-cost biomarker for routine monitoring in diabetic patients. Early identification of inflammation-driven kidney damage may help clinicians intervene before irreversible progression to end-stage renal disease.
Bassami, F., Yavari, M., Feizi, A. et al. Association between high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and diabetic nephropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol 26, 418 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-025-04358-y
Keywords: hs-CRP, diabetic nephropathy, inflammation, diabetic kidney disease, chronic inflammation, risk stratification, BMC Nephrology, kidney complications in diabetes, biomarker research, anti-inflammatory therapy, DN progression
Powered by WPeMatico

A two-drug combination for treating advanced kidney cancer had sustained and durable clinical benefit in more than five years of follow-up, according to a study published in Nature Medicine.
The study reports final clinical data and biomarker analyses from the Phase 3 KEYNOTE-426 trial, which compared the drug combination pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus the single drug sunitinib for patients with previously untreated advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma, the most common type of kidney cancer.
“KEYNOTE-426 was the first trial to combine a PD-1 inhibitor immunotherapy (pembrolizumab) with a VEGF receptor inhibitor antiangiogenic drug (axitinib) in the first-line setting for advanced renal cell carcinoma. It therefore has the longest follow-up duration among the various trials comparing these types of drug combinations,” said Brian Rini, MD, a medical oncologist at Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center and the study’s lead and corresponding author.
Immunotherapy drugs like pembrolizumab stimulate the immune system to kill tumor cells. VEGF receptor inhibitors like axitinib and sunitinib block angiogenesis — the development of blood vessels that tumors need to grow and spread. Pembrolizumab plus axitinib and other immunotherapy-antiangiogenic drug combinations are now standard first-line treatments for advanced kidney cancer.
“Before the development of antiangiogenic drugs and immunotherapies, advanced renal cell carcinoma had a very poor prognosis. These drug combinations have dramatically improved treatment options and outcomes for patients,” said Rini, Ingram Professor of Cancer Research and Thomas F. Frist Sr. Professor of Medicine.
The first interim analysis of outcomes from KEYNOTE-426, published Feb. 16, 2019, in the New England Journal of Medicine, demonstrated that trial participants treated with pembrolizumab plus axitinib had longer overall and progression-free survival, and higher objective response rates compared to those taking sunitinib. The median follow-up was 12.8 months.
Now, with a median follow-up of 67.2 months, the current analysis confirms and extends the interim analysis and provides valuable information about biomarkers that could help guide treatment decisions.
The study in Nature Medicine reports that pembrolizumab plus axitinib had longer overall survival (47.2 months versus 40.8 months for sunitinib) and longer progression-free survival (15.7 months versus 11.1 months for sunitinib). The objective response rate was 60.6% for pembrolizumab plus axitinib and 39.6% for sunitinib.
The researchers reported a variety of associations between the expression of biomarkers and outcomes (overall survival, progression-free survival, objective response rate). The biomarkers they evaluated included an 18-gene T-cell-inflamed expression profile, angiogenesis signature, and PD-1 ligand expression.
“There is an unmet need for biomarkers that are predictive of patient outcomes following treatment with available first-line therapies for advanced renal cell carcinoma,” Rini said. “Although our analysis showed potential clinical utility of some RNA signatures in identifying patients who are likely to benefit the most from each treatment, further prospective clinical studies are needed.”
Pembrolizumab plus axitinib is a first-line treatment option for patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma regardless of biomarker subtypes, he noted.
Reference:
Rini, B.I., Plimack, E.R., Stus, V. et al. Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma: 5-year survival and biomarker analyses of the phase 3 KEYNOTE-426 trial. Nat Med (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-025-03867-5.
Powered by WPeMatico
