FDA approves Laser system for long term treatment of inflammatory acne
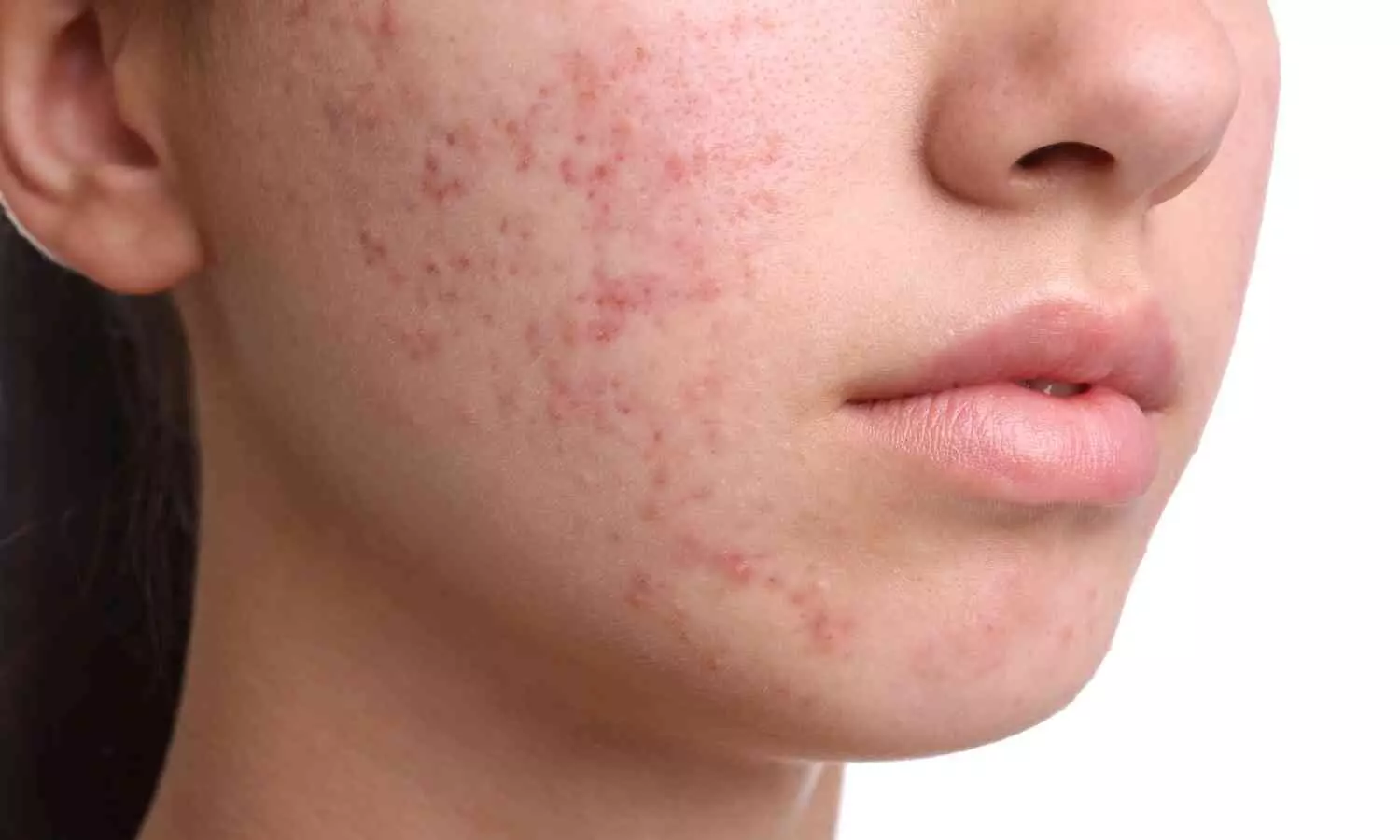
The US Food and drugs administration has approved Accure Laser System that is indicated for long term treatment of patients known to have mild to severe inflammatory acne vulgaris.
The Accure Laser System unlocks the unique selectivity of the 1726 nm laser wavelength, adding proprietary and first-in-class technology to precisely control thermal gradient depth to have maximum impact on the sebaceous gland. This treat-to-temperature mechanism of action has been validated through multiple IRB-approved clinical trials in the United States, achieving an average inflammatory lesion count reduction of 70% at 6 months after a series of four treatments spaced about one month apart. This was observed for all skin types and severities of acne.
Accure Acne recently completed a limited commercial release earlier this year in the United States, delivering significant clinical outcomes, as well as consistent provider and patient satisfaction scores of over 4.4 out of 5. Since then, Accure has expanded the availability of the Accure Laser System in multiple regions, with first adopters in the Middle East, Europe, The Caribbean, and Asia Pacific, where patients of all severities and skin types can benefit from a safe, effective, and now durable clinical outcome.
“This accomplishment is a testament to the relentless pursuit of this goal by Accure, Quanta System, and the team of clinicians and researchers who have spent many years together to bring the Accure Laser to the world”, added Emil Tanghetti, MD, Founder of The Center for Dermatology and Laser Surgery in Sacramento, CA, and the first Accure Laser investigator in the world. “Our journey in understanding the unique nature of this wavelength and the clinical requirements needed to deliver significant clinical outcomes was certainly challenging. The technical innovations of using temperature as an endpoint, combined with forced air cooling and real-time monitoring algorithms has produced a solution that stands alone from more traditional power-based methods. This unique laser has a platform that can be modified and adjusted to possibly treat a number of other skin conditions. I am excited about the future of this device and technology.”
Powered by WPeMatico