Actress Mallika Sukumaran highlights Importance of Early Diagnosis in Fight Against Breast Cancer
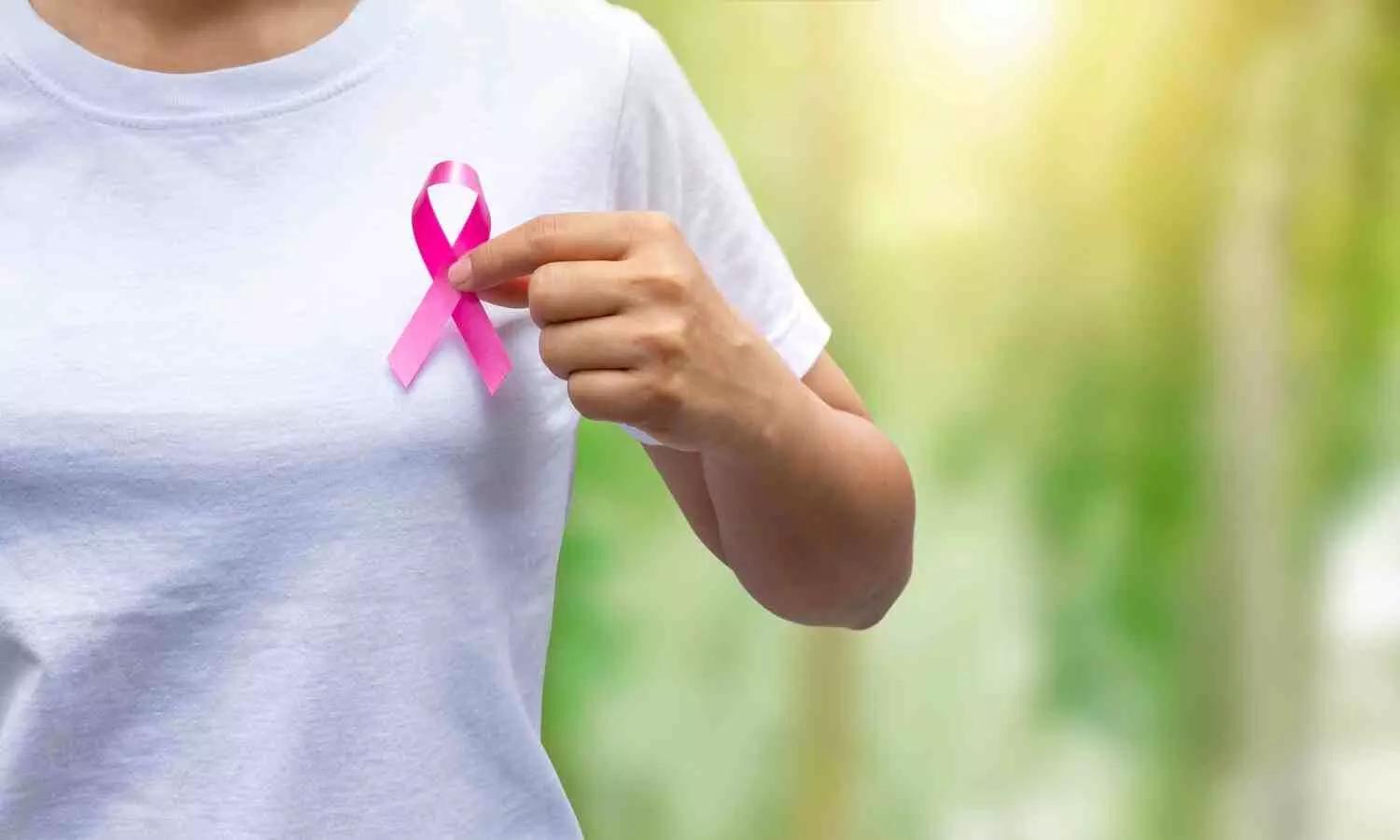

Thiruvananthapuram: Renowned actor Mallika Sukumaran emphasized the critical importance of early detection in the fight against breast cancer, urging women to overcome their reluctance towards regular medical check-ups.
Speaking at the release of the book ‘Breast Cancer: Things to Know’, authored by Dr Chandramohan K (Senior Surgical Oncologist), Dr Boben Thomas (Senior Medical Oncologist), Dr. Ajai Sasidhar (Surgical Oncologist), and Dr. Teena Nelson (Radiation Oncologist), at the newly operational SP Medifort Hospital, she pointed out that Kerala ranks highest in the number of breast cancer patients in India, news agency UNI reported.
The disease, which is the most prevalent form of cancer among women, can be successfully treated if detected early, she noted, urging both government and private institutions to enhance awareness initiatives and create a comprehensive database on breast cancer cases.
Also Read:174-bed cancer hospital coming up at cost of Rs 213 crores in Bandra West
Expressing concern over the increasing number of patients, SP Medifort Chairman and Managing Director Dr SP Asokan assured that the hospital would intensify efforts to raise awareness about breast cancer, underscoring the need for collective action to tackle the issue.
Joint Chairman & Managing Director, SP Subramonian also addressed the gathering, stressing the importance of early diagnosis.
“We must not assume that a cancer diagnosis is a point of no return. The will to detect the disease early and fight it is crucial,” he said, adding that SP Medifort has one of the best-equipped oncology departments in Kerala, offering advanced treatment facilities and expert care.
SP Medifort Executive Directors Dr. S Aathithya and Advaith A Bala spoke at this public event which was attended by a large gathering of medical students, doctors, patients and cancer survivors.
In a bid to promote early detection, SP Medifort Hospital has initiated a free breast cancer screening camp since 1st October, with individuals and organizations encouraged to register for a “free oncologist consultation and also avail 20 percent discount on investigations and advanced cancer health checkups, for October” said Tanjai Kapoor, Chief Marketing Officer, SP Medifort.
The hospital’s cancer survivor association, Cancer Warriors, continues to actively campaign and raise awareness about the disease, providing support and information to patients and their families, he said.
Also Read:CM Sukhu inaugurates tertiary cancer hospital building built at cost of Rs 13.50 crore
Powered by WPeMatico