Tale of Two: Study Unraveling Mystery of TRAP Sequence in Monochorionic Twins
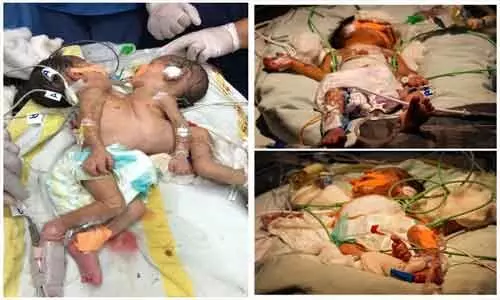
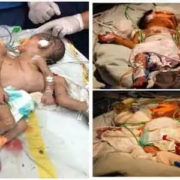
Twin reversed arterial perfusion (TRAP) sequence is a rare and serious complication primarily observed in monochorionic monoamniotic (MCMA) twins, manifesting with acute impacts on both twins involved. With a historically low incidence of approximately 1%, the advent of advanced ultrasonography and assisted reproductive technologies may increase the observed frequency, potentially up to 1 in 40 MC twin pregnancies. Notably, about 30% of cases emerge specifically in MCMA gestations, while conjoined twins, a rare subtype of monochorionic twins, present an even lower incidence. TRAP sequence’s defining characteristic is the dependency of the acardiac twin on the cardiac output of the pump twin, facilitated through unique vascular connections typically identifiable via prenatal ultrasound. A recent investigation showcases an unusual instance of the TRAP sequence linked to conjoined twins, where the acardiac twin was supplied with blood through a direct branch originating from the aortic arch of the pump twin.
Mortality and Management Strategies
The condition exhibits alarmingly high mortality rates, with spontaneous miscarriage rates reaching 35-50% and the risk of pump twin mortality estimated at 30% by 18 weeks gestation without intervention. Effective management strategies aim to prolong gestation and circumvent severe complications, such as fetal hydrops and heart failure. Common interventions comprise expectant monitoring, radiofrequency ablation (RFA), and laser coagulation, with RFA gaining favor due to its minimally invasive nature and potential for improved outcomes. The optimal window for intervention remains under investigation, generally advocated at 14-18 weeks of gestation, although recent insights suggest the potential advantages of even earlier intervention.
Case Study and Intervention Outcomes
A case studied illustrated a unique variation in TRAP sequence wherein the acardiac twin was perfused through a direct branch from the pump twin’s aortic arch. Utilizing RFA effectively occluded this abnormal blood supply, leading to a successful pregnancy outcome. Post-procedure evaluations demonstrated stable hemodynamics in the pump twin post-ablation, allowing for a healthy delivery at 35 weeks with a normal birth weight and Apgar score, reinforcing the utility of timely intervention and the importance of multidisciplinary collaboration throughout management.
Evaluation of Treatment Efficacy
Subsequent evaluations indicated significant regression in size of the acardiac twin following intervention, underscoring the benefits of individualized treatment strategies. Furthermore, systematic reviews support a marked improvement in survival rates through timely interventions, particularly with RFA. Despite limitations such as a small sample size and the absence of late-gestation fetal brain MRI assessments, the findings present valuable insights into the importance of early diagnostics and a tailored approach for improved outcomes in high-risk pregnancies, advocating for future studies integrating larger datasets and machine learning techniques for enhanced decision-making.
Key Points
– -Incidence and Classification-: TRAP sequence predominantly occurs in monochorionic monoamniotic (MCMA) twin pregnancies, with an estimated incidence of approximately 1%, which may increase to 1 in 40 due to advancements in ultrasound and reproductive technologies. About 30% of cases occur within MCMA gestations, while conjoined twins represent a rarer variant.
– -Pathophysiology-: The defining feature of TRAP sequence is the reliance of the acardiac twin on the pump twin’s cardiac output through anomalous vascular connections, typically visualized via prenatal ultrasound.
– -Mortality Rates-: TRAP sequence is associated with high mortality rates, exhibiting a spontaneous miscarriage rate of 35-50% and a 30% risk of mortality for the pump twin by 18 weeks gestation in the absence of intervention.
– -Management Strategies-: Treatment focuses on prolonging gestation and avoiding complications like fetal hydrops and heart failure. Effective interventions include expectant management, radiofrequency ablation (RFA), and laser coagulation, with RFA being preferable due to its minimally invasive nature. The optimal intervention window is generally recommended between 14-18 weeks, though earlier intervention may be beneficial.
– -Case Study Outcomes-: A case study exemplified a variation where the acardiac twin was perfused via a directly connected branch from the pump twin’s aorta. The application of RFA successfully occluded this supply, leading to positive hemodynamic stability for the pump twin, resulting in delivery at 35 weeks with normal birth metrics, emphasizing the need for timely and collaborative intervention.
– -Efficacy and Future Directions-: Post-intervention assessments showed significant reduction in the size of the acardiac twin, indicating the effectiveness of tailored treatment. Systematic reviews highlight improved survival rates with timely interventions like RFA, though limitations exist regarding sample sizes and imaging assessments. Future research should expand datasets and incorporate machine learning methods to refine clinical decision-making in these complex scenarios.
Reference –
Hua Lai et al. (2025). Individualized Intervention And Growth Dynamics Assessment In TRAP Sequence With Conjoined Twins Based On Radiofrequency Ablation. *BMC Pregnancy And Childbirth*, 25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-025-07658-1.
Powered by WPeMatico