New study analyzes link between digit ratio and oxygen consumption in soccer players
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico

Cambridge: AstraZeneca’s Tagrisso (osimertinib) with the addition of chemotherapy has been approved in the US for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated (EGFRm) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
The approval following a Priority Review by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) was based on the results from the FLAURA2 Phase III trial published in The New England Journal of Medicine. Tagrisso with the addition of chemotherapy reduced the risk of disease progression or death by 38% compared to Tagrisso monotherapy which is the 1st-line global standard of care (hazard ratio [HR] 0.62; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.49-0.79; p<0.0001). Median progression-free survival (PFS) by investigator assessment was 25.5 months for patients treated with Tagrisso plus chemotherapy, an 8.8-month improvement versus Tagrisso monotherapy (16.7 months).
PFS results from blinded independent central review (BICR) were consistent with the results by investigator assessment, showing 29.4 months median PFS with Tagrisso plus chemotherapy, a 9.5-month improvement over Tagrisso monotherapy (19.9 months) (HR 0.62; 95% CI 0.48-0.80; p=0.0002).
Each year in the US, there are over 200,000 people diagnosed with lung cancer, and 80-85% of these patients are diagnosed with NSCLC, the most common form of lung cancer. Approximately 70% of people are diagnosed with advanced NSCLC. Additionally, about 15% of NSCLC patients in the US have an EGFR mutation.
Pasi A. Jänne, MD, PhD, medical oncologist at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and principal investigator for the trial, said, “This approval based on the unprecedented data from FLAURA2 brings a critical new treatment option to patients with advanced EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Now, with the choice of two highly effective osimertinib-based options, physicians can better tailor treatment to an individual’s needs and help ensure the best possible outcome for each patient.”
Dave Fredrickson, Executive Vice President, Oncology Business Unit, AstraZeneca, said, “This important new treatment option can delay disease progression by nearly nine additional months, establishing a new benchmark with the longest reported progression-free survival benefit in the 1st-line advanced setting. This approval reinforces Tagrisso as the backbone of EGFR-mutated lung cancer treatment either as monotherapy or in combination with chemotherapy. This news is especially important for those with a poorer prognosis, including patients whose cancer has spread to the brain and those with L858R mutations.”
Laurie Ambrose, President and CEO, GO2 for Lung Cancer, said, “We are so excited to see this continued progress advancing more personalized treatment options for our community. The more we can target the right treatments for the right people at the right time, the better outcomes will be for our community – a goal we all collectively share.”
Results from a prespecified exploratory analysis of patients in the FLAURA2 trial with brain metastases at baseline showed Tagrisso plus chemotherapy reduced the risk of central nervous system (CNS) disease progression or death by 42% compared to Tagrisso alone (HR 0.58; 95% CI 0.33-1.01) as assessed by BICR. With two years of follow up, 74% of patients treated with Tagrisso plus chemotherapy had not experienced CNS disease progression or death versus 54% of patients treated with Tagrisso monotherapy.
While the overall survival (OS) results remained immature at the second interim analysis (41% maturity), no trend towards a detriment was observed (HR 0.75; 95% CI 0.57-0.97). The trial continues to assess OS as a key secondary endpoint.
The safety profile of Tagrisso with the addition of chemotherapy was generally manageable and consistent with the established profiles of the individual medicines. Adverse event (AE) rates were higher in the Tagrisso plus chemotherapy arm, driven by well-characterised chemotherapy-related AEs. Discontinuation rates for Tagrisso due to AEs were low in both arms of the trial (11% for Tagrisso plus chemotherapy and 6% for monotherapy).
In December 2023, osimertinib (Tagrisso) with the addition of chemotherapy was added to the NCCN Clinical Practical Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines) as a NCCN Category 1 Other Recommended regimen for patients with NSCLC whose tumours have EGFR exon 19 deletion or exon 21 L858R mutations based on the data from FLAURA2.
The US regulatory submission was reviewed under Project Orbis, which provides a framework for concurrent submission and review of oncology medicines among participating international partners. As part of Project Orbis, Tagrisso in combination with chemotherapy is also under review by regulatory authorities in Australia, Canada, and Switzerland. Regulatory applications are also under review in several other countries based on the FLAURA2 results.
Tagrisso is approved as monotherapy in more than 100 countries including in the US, EU, China and Japan. Approved indications include for 1st-line treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic EGFRm NSCLC, locally advanced or metastatic EGFR T790M mutation-positive NSCLC, and adjuvant treatment of early-stage EGFRm NSCLC.
“As part of AstraZeneca’s ongoing commitment to treating patients as early as possible in lung cancer, Tagrisso is also being investigated in the neoadjuvant setting in the NeoADAURA Phase III trial with results expected later this year, and in the early-stage adjuvant resectable setting in the ADAURA2 Phase III trial,” the release stated.
Read also: AstraZeneca, BioInvent ink pact to evaluate BI-1206 in combo with rituximab, Calquence
Powered by WPeMatico
In
the late 18th century, smallpox was a major public health problem. It
was a highly contagious viral disease that killed millions.
There was no known cure for smallpox, In
1796, an English physician named Edward Jenner developed a new vaccine for
smallpox. Jenner noticed cowpox-exposed milkmaids
gained immunity against smallpox, he hypothesized that cowpox could be used
to protect people from smallpox. He tested his hypothesis by inoculating a
young boy named James Phipps with cowpox. Phipps developed a mild case of cowpox, but
he recovered fully. Two months later, Jenner inoculated Phipps
with smallpox, Phipps did not get smallpox, proving that
the vaccine was effective. Jenner’s smallpox vaccine was a major
breakthrough.
It was the first vaccine ever developed,
and it saved millions of lives.
Powered by WPeMatico

New Delhi: India is set to witness its first Helicopter Emergency Medical Service (HEMS) which will operate from All India Institute for Medical Sciences (AIIMS) in Rishikesh.
Through HEMS, the government intends to expand medical outreach and access to trauma care services to a wider population across the country using helicopters.
Aviation Minister Jyotiraditya Scindia assured Uttarakhand Chief Minister Pushkar Dhami of the new integrated airport building of Uttarakhand airport.
Also Read:Govt plans to develop helipads along major highways for medical emergencies
Scindia affirmed, “The request for the HEMS from AIIMS Rishikesh is underway, with helicopter assembly and certification progressing, under my oversight.”
The new Helicopter Emergency Medical Services (HEMS) would operate under project ‘Sanjeevani’ with a coverage radius of 150 kilometers.
Highlighting the importance of the HEMS, Scindia emphasized, “Once operational, helicopters will be stationed at AIIMS Rishikesh, covering a 150 km radius. This will ensure timely transportation of accident victims and patients from hilly terrain to AIIMS.”
Additionally, Scindia announced the commencement of another project, responding to the state government’s request for air connectivity from Hindon Air Base to Pithoragarh.
He stated, “The bidding process for this route has been completed, and the specific route will be awarded after further investigation under UDAN.”
These two announcements are poised to be game-changers for Uttarakhand, given the challenging terrain. Once implemented, the projects will significantly benefit the people of Uttarakhand.
The emergency helicopter services will be indispensable for saving patients during the critical ‘golden hour,’ soon after an accident, when expert medical care is vital. This initiative will be a boon for Uttarakhand, a state that attracts tourists, pilgrims, and adventure enthusiasts annually, while also contending with natural disasters.
Powered by WPeMatico

Sleep is critical for our overall well-being,
which is fundamental in maintaining brain health and cognitive function.
Adequate sleep supports memory consolidation, emotional regulation, and optimal
decision-making, ultimately enhancing productivity and quality of life.
To a
large extent, the amount of sleep determines our brain health. But it is worth
noting that our sleep requirements vary as we age. Typically, a newborn baby up
to the age of a toddler requires 11-17 hours of sleep, while adults need 7-8
hours of sleep.
However, a staggering 60-70% of our adult population fails to
get this amount of sleep due to our current fast-paced lifestyles and excessive
screen time.
The reduction in sleep time significantly
impacts our overall health, but our brain is affected the most. Our brain is a
vital organ that controls our thoughts, memory, motor skills, and vision,
coordinates our movements, and helps us with judgment, reasoning, and thinking.
All these functions start deteriorating as we age, but lack of sleep can harm
our brain functions.
With prolonged sleep deprivation, our brain starts to slow
down and become susceptible to neurodegenerative processes.
Let’s look at some benefits sleep can have on
our brain health.
Importance of sleep for good brain health
Restores body cells: During
the restorative phase of sleep, the body initiates crucial repair and
rejuvenation processes at the cellular level. This period is characterised by
the release of growth hormones, like human growth hormone (HGH), which is
pivotal in stimulating tissue repair, promoting muscle growth, and enhancing
immune function. These growth hormones facilitate the repair of damaged cells
and tissues, aiding recovery from daily wear and tear. Furthermore, the immune
system is bolstered during sleep, with immune cells actively targeting and
combating pathogens to defend against infections and illnesses. Sleep is a
vital time for the body to replenish and revitalise itself, ensuring optimal
physical health and resilience.
Removes toxic waste: Rapid
eye movement (REM) while sleeping is the stage where people experience dreams.
REM is also the critical stage where toxic waste from the brain is cleared.
Amyloid beta, tau proteins, and other metabolic waste accumulated during the
daytime get removed from the brain. When toxins are not cleared from the brain,
it leads to various diseases like brain fog, an inability to focus, reduction
in cognitive abilities, and, in the long term, can even lead to neurological
conditions like dementia.
Memory consolidation: During
sleep, the brain actively processes and consolidates the day’s information,
sharpening problem-solving skills and fostering creativity. This dynamic
process strengthens neural connections, enhances memory retention and facilitates
innovative thinking. In essence, sleep serves as a crucial phase for optimising
cognitive functions and promoting creative problem-solving.
Improves cognitive functions & provides
emotional stability: Sleep is vital for brain health, facilitating
cognitive functions like memory consolidation and learning. Inadequate sleep is
also detrimental to promoting emotional well-being, as sleep regulates mood and
reduces stress, anxiety, and depression.
Improves metabolic functions of the
body: Quality sleep plays a role in regulating the metabolic functions of the
body. Adequate rest supports the balance of hormones involved in metabolism,
such as insulin, leptin, and ghrelin, which helps control appetite and energy
expenditure. Additionally, sufficient sleep promotes efficient glucose
metabolism, reduces the risk of insulin resistance, and supports healthy weight
management. Therefore, prioritising good sleep habits is essential for
optimising metabolic health and overall well-being.
How do you ensure you get the right amount of
sleep?
Adopting a few effective sleep practices helps
unlock the benefits of restorative sleep.
Disclaimer: The views expressed in this article are of the author and not of Medical Dialogues. The Editorial/Content team of Medical Dialogues has not contributed to the writing/editing/packaging of this article.
Powered by WPeMatico

New Delhi: In a notable development of the Kayakalp facilities, the count of Public Health Facilities up to District Hospitals, has witnessed a substantial rise, soaring from 97 in the fiscal year 2015-16 to an impressive 13,915 in the fiscal year 2021-22.
The evolving landscape introduced a new thematic dimension in the criteria for these facilities in 2021-22, emphasizing the adoption of eco-friendly practices.
Adding to the transformative measures, the Kayakalp scheme has undergone a noteworthy transition, now being classified as an “incentive scheme.” This initiative operates on dual fronts, encompassing Public Health Facilities up to District Hospitals and Central Government Hospitals. The expansion in the number of facilities underscores the government’s commitment to enhancing public healthcare infrastructure, ensuring wider accessibility and improved services. The incorporation of an eco-friendly aspect reflects a growing emphasis on sustainable and environmentally conscious practices within the healthcare domain.
Also Read: Kayakalp Team pays visit to AIIMS Bhubaneswar
The Kayakalp scheme’s reclassification as an incentive scheme underscores the intention to motivate and reward excellence in maintaining high standards of cleanliness, hygiene, and overall quality in public health facilities. This multifaceted approach aims to create a healthier, more sustainable healthcare environment at both district and central government levels.
For Public Health facilities upto district Hospitals, the assessment tool has a checklist arranged around eight thematic areas including Hospital/Facility Upkeep, Sanitation and Hygiene, Waste Management, Infection Control, Support Services, Hygiene Promotion, Cleanliness beyond hospital boundary wall and Eco-friendly facility. For Central Government Hospitals, the assessment tool has the following thematic areas including Hospital Upkeep, Sanitation and hygiene, Support Services, Waste Management, infection Control, Hygiene Promotion and Feedback Mechanism from Public on Cleanliness.
Also Read: Phagwara’s Rajan Eye Care Hospital gets recognition under cleanliness survey
Powered by WPeMatico

New Delhi: Pharmaceuticals firm Wockhardt Ltd has reported narrowing of consolidated net loss to Rs 86 crore for the third quarter ended December 31, 2023.
Revenue from operations during the quarter under review stood at Rs 701 crore as compared to Rs 699 crore in the year-ago period, the company said.
Total expenses were lower at Rs 796 crore as against Rs 803 crore in the same period last fiscal.
Read also: Wockhardt Gets CDSCO Panel Nod To study combination of cefepime and zidebactam
Headquartered in Mumbai, Wockhardt is an Indian pharmaceutical and biotechnology company. The Company produces biopharmaceuticals, nutrition products, formulations, vaccines and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Its manufacturing plants are located in India, UK, Ireland, France and US, and subsidiaries in US, UK, Ireland and France.
Powered by WPeMatico
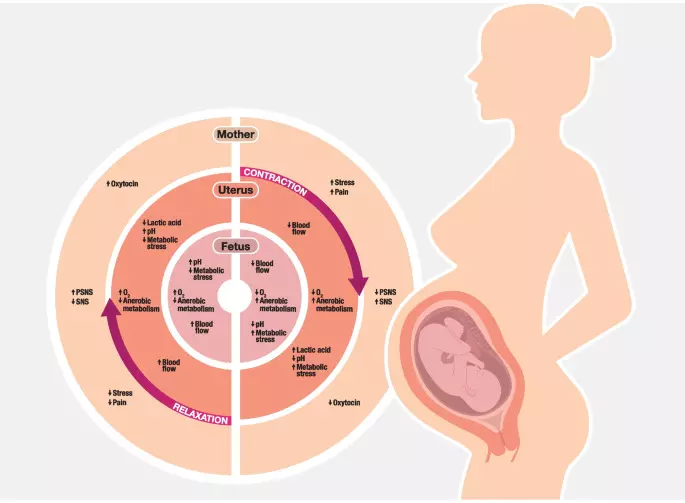
High cumulative oxytocin doses during labour tied to adverse postpartum outcomes suggests a new study published in the European Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology and Reproductive Biology.
The reproductive hormone oxytocin facilitates labour, birth and postpartum adaptations for women and newborns. Synthetic oxytocin is commonly given to induce or augment labour and to decrease postpartum bleeding. A study was done to systematically review studies measuring plasma oxytocin levels in women and newborns following maternal administration of synthetic oxytocin during labour, birth and/or postpartum and to consider possible impacts on endogenous oxytocin and related systems.
Systematic searches of PubMed, CINAHL, PsycINFO and Scopus databases followed PRISMA guidelines, including all peer-reviewed studies in languages understood by the authors. Thirty-five publications met the inclusion criteria, including 1373 women and 148 newborns. Studies varied substantially in design and methodology, so classical meta-analysis was not possible. Therefore, results were categorized, analysed and summarised in text and tables. Results: Infusions of synthetic oxytocin increased maternal plasma oxytocin levels dose-dependently; doubling the infusion rate approximately doubled oxytocin levels. Infusions below 10 milliunits per minute (mU/min) did not raise maternal oxytocin above the range observed in physiological labour. At high intrapartum infusion rates (up to 32 mU/min) maternal plasma oxytocin reached 2–3 times physiological levels. Postpartum synthetic oxytocin regimens used comparatively higher doses with shorter duration compared to labour, giving greater but transient maternal oxytocin elevations. Total postpartum dose was comparable to the total intrapartum dose following vaginal birth, but post-caesarean dosages were higher. Newborn oxytocin levels were higher in the umbilical artery vs. umbilical vein, and both were higher than maternal plasma levels, implying substantial fetal oxytocin production in labour. Newborn oxytocin levels were not further elevated following maternal intrapartum synthetic oxytocin, suggesting that synthetic oxytocin at clinical doses does not cross from mother to fetus. Synthetic oxytocin infusion during labour increased maternal plasma oxytocin levels 2–3-fold at the highest doses and was not associated with neonatal plasma oxytocin elevations. Therefore, direct effects from synthetic oxytocin transfer to the maternal brain or fetus are unlikely. However, infusions of synthetic oxytocin in labour change uterine contraction patterns. This may influence uterine blood flow and maternal autonomic nervous system activity, potentially harming the fetus and increasing maternal pain and stress.
Reference:
Buckley S, Uvnäs-Moberg K, Pajalic Z, Luegmair K, Ekström-Bergström A, Dencker A, Massarotti C, Kotlowska A, Callaway L, Morano S, Olza I, Magistretti CM. Maternal and newborn plasma oxytocin levels in response to maternal synthetic oxytocin administration during labour, birth and postpartum – a systematic review with implications for the function of the oxytocinergic system. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023 Mar 2;23(1):137. doi: 10.1186/s12884-022-05221-w. PMID: 36864410; PMCID: PMC9979579.
Keywords:
High cumulative oxytocin doses, labour, adverse postpartum outcomes, European Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology and Reproductive Biology, Buckley S, Uvnäs-Moberg K, Pajalic Z, Luegmair K, Ekström-Bergström A, Dencker A, Massarotti C, Kotlowska A, Callaway L, Morano S, Olza I, Magistretti CM, Oxytocin, Maternal oxytocin, Newborn oxytocin, Synthetic oxytocin, Pitocin, Syntocinon, Postpartum oxytocin, Induction of labour, Augmentation of labour
Powered by WPeMatico
