Elevated glutamine triggers stroke risk in moyamoya disease via endothelial‐to‐mesenchymal transition, finds study
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico

Faridabad: The oxygen production plant at Badshah Khan (BK) Civil Hospital, which has been out of service for approximately six months, has raised significant concerns among healthcare officials and patients. Despite boasting state-of-the-art in-house production capacity, the hospital has been compelled to source oxygen from external suppliers due to the plant’s non-operational status.
Sources within the health department revealed that the 200-bed hospital, one of the largest government healthcare facilities in the state, has encountered difficulties in oxygen supply since the 1,000 litres per minute (LPM) oxygen plant ceased production last year due to technical issues. While authorities have initiated efforts to address the matter, the plant remains inactive, creating a crisis of oxygen in the hospital.
According to The Tribune, one of the employees stated, “The purity level of oxygen, which should be 92 per cent or above, has been much lower due to issues related to damaged parts or the upkeep of the machinery.” Although the plant possesses the capability for oxygen production, sources allege that substandard or low purity levels render the oxygen unusable for medical purposes. Improper distillation processes have resulted in elevated impurity levels, rendering the gas unfit for patient care. Notably, the plant was established under a Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiative during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2021.
However, the absence of an annual maintenance contract (AMC) with the responsible company or agency has hindered timely repairs. The estimated cost of the AMC was approximately Rs 5 lakh. Consequently, the plant’s malfunction has also contributed to the poor upkeep of flow meters and oxygen supply points throughout the hospital, with many units lying non-functional, reports the Daily.
Despite these challenges, Dr Savita Yadav, Principal Medical Officer (PMO) of the civil hospital, reassured that there is no shortage of oxygen supply within the facility. Dr Yadav stated that the hospital procures 40 to 50 Type-D cylinders of gas from external sources each month, a solution deemed more economically viable. Additionally, oxygen is sourced from another in-house plant with a capacity of 200 LPM, albeit without a piped supply. The decision regarding the AMC lies with the authorities at the head office, according to Dr Yadav. The BK Civil Hospital, which caters to over 2,200 outpatients and nearly 100 emergency cases daily, emphasizes the critical need for operational oxygen infrastructure to ensure uninterrupted healthcare delivery.
Also Read: Cancer patient dies after disruption in oxygen supply; Doctor, Nurses Suspended
Powered by WPeMatico
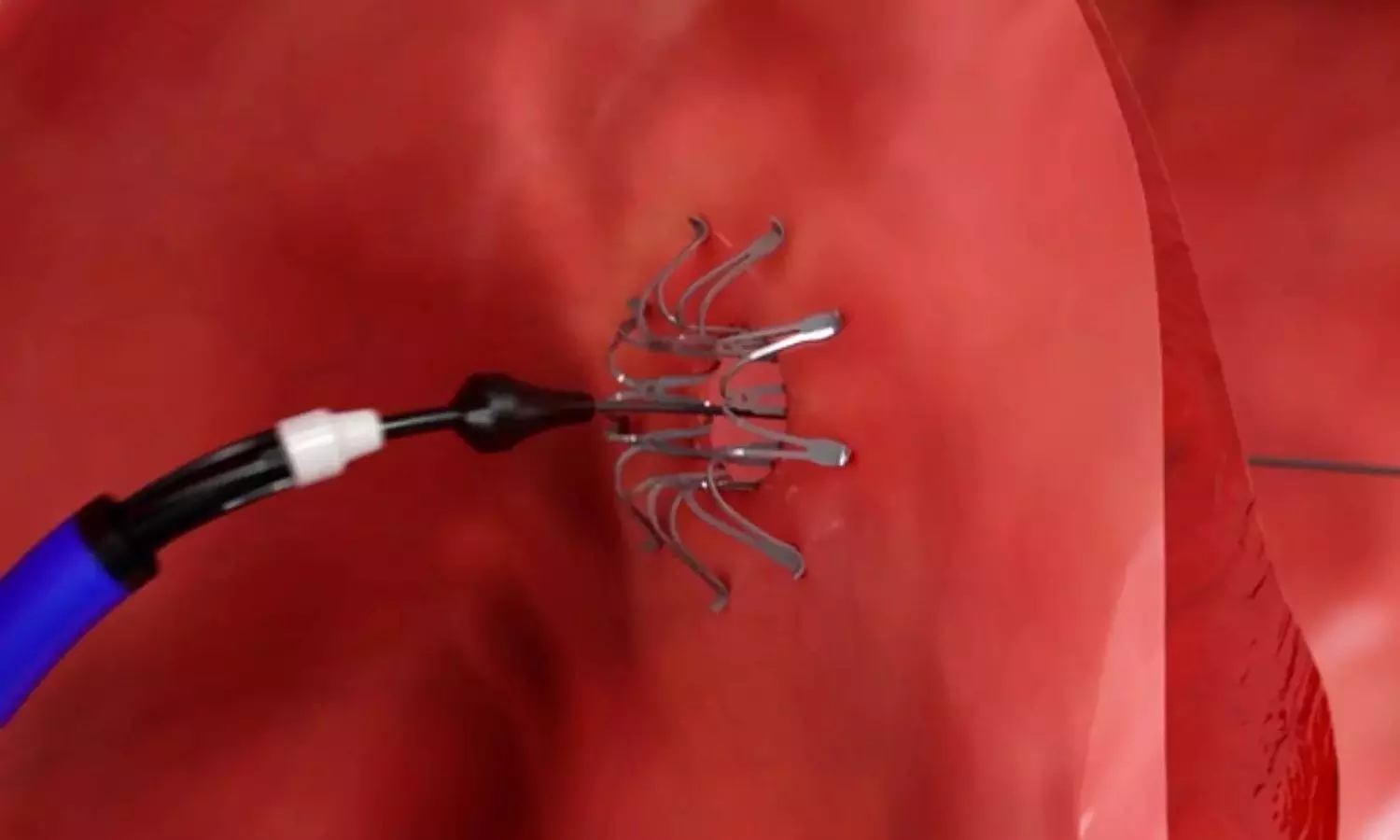
USA: Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) presents a complex clinical challenge, with limited treatment options compared to heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). However, recent advancements in medical technology have sparked hope in the form of atrial shunt devices, offering a novel approach to managing HFpEF.
The post hoc analysis of REDUCE LAP-HF II Randomized Clinical Trial sheds light on the long-term effect of an atrial shunt device on cardiac structure and function in patients with heart failure and preserved or mildly reduced ejection fraction.
The study findings published in JAMA Cardiology showed no evidence of right ventricle (RV) dysfunction over the initial two years and supported the previously identified responder group hypothesis.
“The post hoc analysis of the REDUCE LAP-HF II RCT comprising 621 patients found that atrial shunting led to reverse remodeling of left-sided chambers and increases in volume of right-sided chambers but no change in RV systolic function compared with sham,” the researchers wrote.
They found changes in cardiac function/structure to be favorable in previously defined responders versus the nonresponders.
The results of the REDUCE LAP-HF II trial were neutral overall, however, atrial shunt therapy demonstrated potential efficacy in responders (no latent pulmonary vascular disease and no cardiac rhythm management device). Therefore, Ravi B. Patel, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, Illinois, and colleagues aimed to evaluate the effect of atrial shunt vs sham control on cardiac structure/function in the overall study and stratified by responder status.
For this purpose, the researcher conducted a sham-controlled randomized clinical trial of an atrial shunt device in HFpEF/HFmrEF. Trial participants with evaluable echocardiography scans were recruited from 89 international medical centers.
The outcome measures were changes in echocardiographic measures from baseline to 1, 6, 12, and 24 months after the index procedure.
The modified intention-to-treat analysis of the REDUCE LAP-HF II trial comprised 621 randomized patients with a median age of 72.0 years; 61.5% were females; shunt arm, 309; sham control arm, 312.
The researchers reported the following findings:
In conclusion, the analysis showed that atrial shunting led to reverse remodeling of left-sided chambers and increases in right-sided chamber volume consistent with the shunt flow but no change in RV systolic function compared with sham.
“Changes in cardiac function/structure were more favorable in responders versus nonresponders treated with the shunt, supporting the previously identified responder group hypothesis and mechanism, although there is a need for further evaluation with longer follow-up,” the researchers wrote.
Reference:
Patel RB, Silvestry FE, Komtebedde J, et al. Atrial Shunt Device Effects on Cardiac Structure and Function in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction: The REDUCE LAP-HF II Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Cardiol. Published online April 17, 2024. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2024.0520
Powered by WPeMatico

Greece: A recent study has shown that acute coronary syndrome (ACS) patients with newly detected diabetes mellitus (NDDM) experience heightened cardiometabolic challenges similar to those with established diabetes mellitus. The findings were published online in Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice on April 08, 2024.
NDDM patients showed lower HDL-C and higher triglyceride levels versus non-DM counterparts, alongside elevated waist circumference and body mass index (BMI). Moreover, they experienced more extensive necrosis compared to patients with established DM.
In the realm of cardiovascular health, the interplay between diabetes mellitus and acute coronary syndrome presents a multifaceted challenge for patients and clinicians alike. Recent studies have shed light on a concerning trend: newly detected diabetes mellitus in ACS patients not only parallels the adverse cardiometabolic profile of those with established diabetes but also signifies a potentially more extensive ischemic myocardial insult. This revelation underscores the critical need for tailored management strategies and heightened vigilance in clinical practice.
The convergence of diabetes mellitus and ACS marks a pivotal intersection of two formidable health concerns. ACS, encompassing conditions such as myocardial infarction and unstable angina, represents acute manifestations of coronary artery disease (CAD), a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Diabetes mellitus, meanwhile, exerts its insidious influence through mechanisms of insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, and systemic inflammation, fostering a milieu ripe for cardiovascular complications.
The impact of newly detected diabetes mellitus on metabolic parameters and the extent of myocardial necrosis in patients with ACS is not fully explored. Loukianos S Rallidis, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, University General Hospital ATTIKON, Athens, Greece, and colleagues examined the impact of NDDM on cardiometabolic characteristics and myocardial necrosis in ACS patients.
CALLINICUS-Hellas Registry is an ongoing prospective multicenter observational study assessing adherence to lipid-lowering therapy (LLT) among ACS patients in Greece. Three groups were created: patients with NDDM (abnormal fasting glucose, HbA1c ≥ 6.5 % and no previous history of DM), b) patients without known diabetes and HbA1c < 6.5 % (non-DM), and c) patients with prior diabetes.
The study led to the following findings:
“Acute coronary syndrome patients with newly detected diabetes mellitus have an adverse cardiometabolic profile similar to patients with prior DM and have more extensive myocardial insult,” the researchers concluded.
Reference:
Rallidis LS, Papathanasiou KA, Tsamoulis D, Bouratzis V, Leventis I, Kalantzis C, Malkots B, Kalogeras P, Tasoulas D, Delakis I, Lykoudis A, Daios S, Potoupni V, Zervakis S, Theofilatos A, Kotrotsios G, Kostakou PM, Kostopoulos K, Gounopoulos P, Mplani V, Zacharis E, Barmpatzas N, Kotsakis A, Papadopoulos C, Trikas A, Ziakas A, Skoularigis I, Naka KK, Tziakas D, Panagiotakos D, Vlachopoulos C. Newly detected diabetes mellitus patients with acute coronary syndrome have an adverse cardiometabolic profile similar to patients with prior diabetes and a more extensive ischemic myocardial insult. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2024 Apr 9;211:111664. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2024.111664. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 38604446.
Powered by WPeMatico
Thane: In a remarkable case, doctors at Wockhardt Hospitals in Thane have successfully treated a one-year-old boy born with multiple complications, including the absence of an anus, officials announced on Wednesday.
Child specialists Bhavesh Doshi and Nitu Mundhra addressed the child’s condition known as ‘Ano Rectal Malformation’ (ARM), which meant the baby lacked a rectal opening. Additionally, the child faced challenges such as tongue-tie, where the tongue was stuck to the floor of the mouth, and Hypospadias, a condition where the urinary outlet is misplaced.
The newborn’s parents — identified as the Salian couple — were shocked to learn of these issues in their first child, whom the doctors admitted to the hospital’s neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), and put on parenteral nutrition as breastfeeding was not feasible, reports IANS.
Mundhra said ARM is rare, seen just once in about a lakh deliveries, and in the delivery room, all the newborn babies are thoroughly examined from head to toe to detect any abnormalities, especially if they are born with a problem.
“In this baby, when we detected ARM, we checked him thoroughly and found the tongue-tie which could affect his feeding and lead to speech difficulties and also Hypospadias. After counselling the parents, the baby underwent multiple surgeries,” said Mundhra.
In this case, after detecting ARM, the medical team identified additional concerns like tongue-tie and Hypospadias. The child underwent five procedures including colostomy, anal reconstruction, and colostomy closure to address ARM issues, alongside procedures for Hypospadias and tongue-tie.
The ARM correction was done in three surgical steps, comprising a temporary opening to allow passage of stool and enable the baby to feed. Two months later, a four-hour-long operation was performed to create a new anus at the normal position, and after two more months, another surgery was performed for colostomy closure.
During this surgery, the opening created in the abdominal wall was closed and the baby now passes motions normally from the opening, said the medicos.
According to an IANS report, Eight months after the surgery, the child underwent a major surgery for Hypospadias to get the urinary opening in the normal position, which was also successful and the child can now pass urine without any difficulty.
Now the child is one year old and functions like other kids of his age after undergoing five surgeries in the first 12 months of his life.
 Also Read:Mumbai doctors successfully treat patient with a Rare Complication of DVT
Also Read:Mumbai doctors successfully treat patient with a Rare Complication of DVT
Powered by WPeMatico
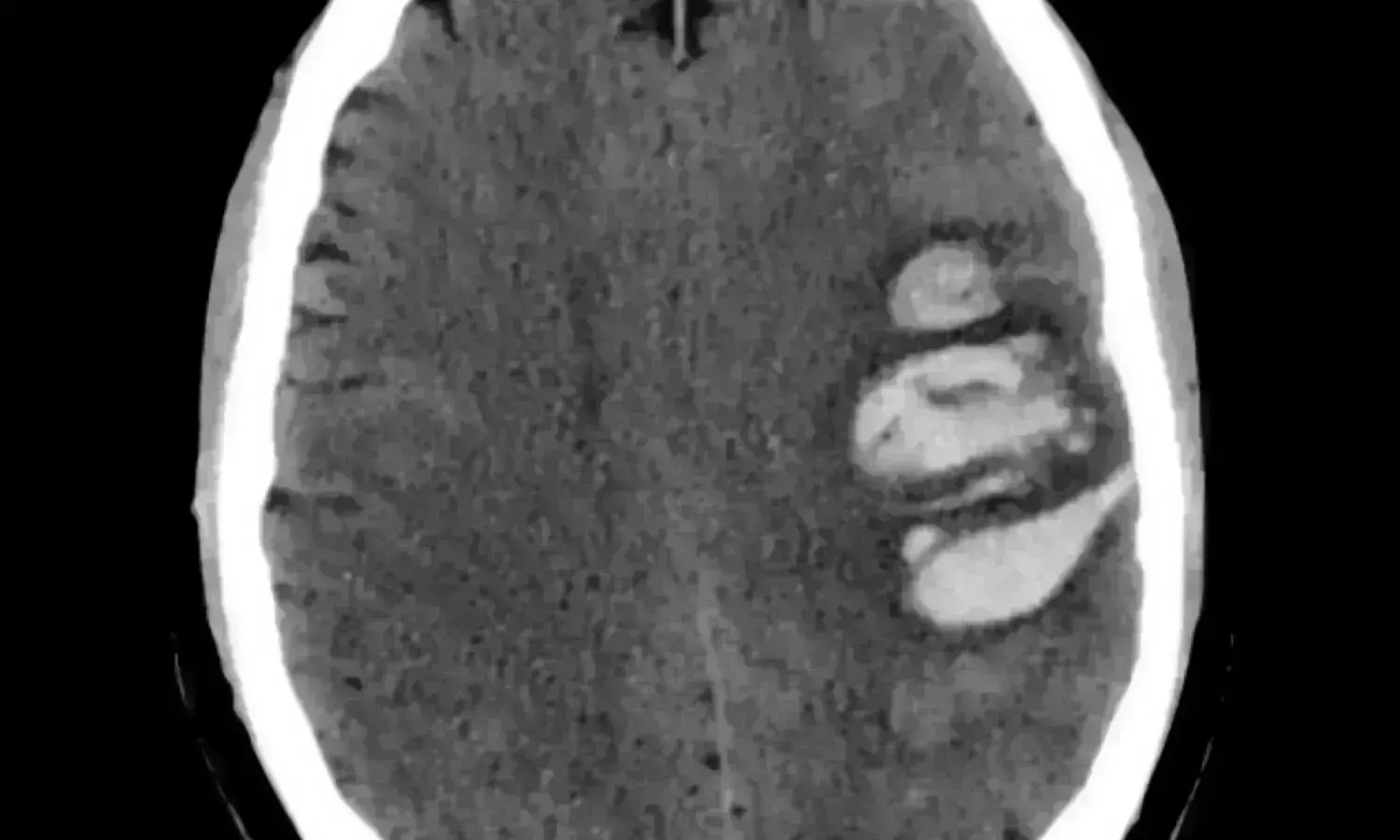
A recent study published in The New England Journal of Medicine found that early minimally invasive surgery to remove brain hemorrhages may lead to better recovery than traditional medical management alone.
This multicenter, randomized trial focused on patients who experienced an acute intracerebral hemorrhage, specifically the individuals with lobar or anterior basal ganglia hemorrhages and had hematoma volumes between 30 to 80 milliliters. The participants were divided into a group receiving minimally invasive surgical removal of the hematoma along with standard medical treatment and another the other group receiving only medical management according to the existing guidelines.
The primary goal of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of surgical intervention in improving the patient outcomes which was measured by the utility-weighted modified Rankin scale. This scale ranges from 0 to 1, where the higher scores signify better functional outcomes according to the patient assessments. A total of 300 patients were enrolled, with the trial noticing an adaptation part-way through after 175 patients had joined where this shift limited further enrollments to only the individuals with lobar hemorrhages due to an observed trend in the data.
The results from the study indicated a notable difference in recovery outcomes. The surgery group had an average score of 0.458 on the modified Rankin scale when compared to 0.374 in the control group 6 months after treatment. This difference was statistically significant and suggested a clear benefit of surgical intervention among the patients with lobar hemorrhages. In this subgroup, the mean score difference was more pronounced at 0.127 in favor of surgery. However, for the individuals with anterior basal ganglia hemorrhages, surgery did not show a notable benefit.
Only 9.3% of patients in the surgery group died within 30 days of enrollment, when compared to 18.0% in the control group which points to the reduction in early mortality rates. This significant decrease illuminates the additional benefit of surgical intervention in managing acute intracerebral hemorrhages. However, the surgical approach evidenced a 3.3% incidence of postoperative complications like rebleeding and neurological deterioration in the surgery group. Overall, these findings suggest that for certain patients with specific types of brain hemorrhages, early minimally invasive surgery could be a beneficial treatment option that offers improved functional outcomes and lower mortality rates.
Reference:
Pradilla, G., Ratcliff, J. J., Hall, A. J., Saville, B. R., Allen, J. W., Paulon, G., McGlothlin, A., Lewis, R. J., Fitzgerald, M., Caveney, A. F., Li, X. T., Bain, M., Gomes, J., Jankowitz, B., Zenonos, G., Molyneaux, B. J., Davies, J., Siddiqui, A., Chicoine, M. R., … Barrow, D. L. (2024). Trial of Early Minimally Invasive Removal of Intracerebral Hemorrhage. In New England Journal of Medicine (Vol. 390, Issue 14, pp. 1277–1289). Massachusetts Medical Society. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa2308440
Powered by WPeMatico
First trimester Use of Hydroxychloroquine in lupus or RA not linked to higher risk of birth defects suggests a new study published in the Rheumatology.
A study was done to assess the infant risk of major congenital malformations (MCM) associated with first-trimester exposure to hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) among mothers with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) or rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This population-based cohort study utilised Swedish nationwide registers and included all singleton births (2006-2021) among individuals with prevalent SLE or RA in Sweden. The exposure was filling ≥1 HCQ prescription during the first trimester. The outcome was infant MCM within one year of birth. Inverse probability of treatment weighting was applied to adjust for potential confounders (e.g. maternal smoking, body mass index, pregestational diabetes, and corticosteroids). Modified Poisson regression models with robust variance estimated risk ratios and 95% confidence intervals (RR 95%CI).
Results: They included 1,007 births (453 exposed) and 2,500 births (144 exposed) in the SLE and RA cohorts, respectively. The MCM risks in the SLE overall cohort, exposed, and unexposed groups were 3.6%, 3.7%, and 3.4%, respectively. The corresponding figures in the RA cohort were 4.4%, 5.6%, and 4.3%, respectively. The adjusted RRs (95%CI) were 1.29 (0.65-2.56) in the SLE cohort, 1.32 (0.56-3.13) in the RA cohort, and 1.30 (0.76-2.23) in the pooled analysis. The adjusted risk difference (exposed vs unexposed) was small (0.9% in SLE and 1.3% in RA). Sensitivity analyses examining different exposure and outcome windows yielded similar findings. First-trimester exposure to HCQ was not associated with a significantly increased risk of MCM. HCQ’s benefits may outweigh the risks in managing SLE or RA during pregnancy.
Reference:
Nguyen NV, Svenungsson E, Dominicus A, Altman M, Hellgren K, Simard JF, Arkema EV. Hydroxychloroquine in lupus or rheumatoid arthritis pregnancy and risk of major congenital malformations: a population-based cohort study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024 Mar 13:keae168. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keae168. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 38479815.
Powered by WPeMatico
