AI risk assessment for CVD effective non-invasive alternative: Study
A new study published in the Npj Digital Medicine journal revealed how the risk assessment system cardiovascular disease (rpCVD) technique may be used to assess CVD risk in primary care settings more quickly, easily, and non-invasively without requiring more involved clinical tests.
The real-world adoption of CVD risk assessment remains below ideal, even though there are well-validated instruments for assessing this risk, such as the pooled cohort equations (PCE) for American populations and the QRISK3 and SCORE2 for European populations. This project evaluated an automated retinal photography and artificial intelligence (AI)-based rpCVD in primary care settings in Australia for real-world accuracy (primary result), practicality, and acceptance (secondary objectives).
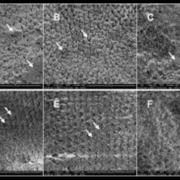
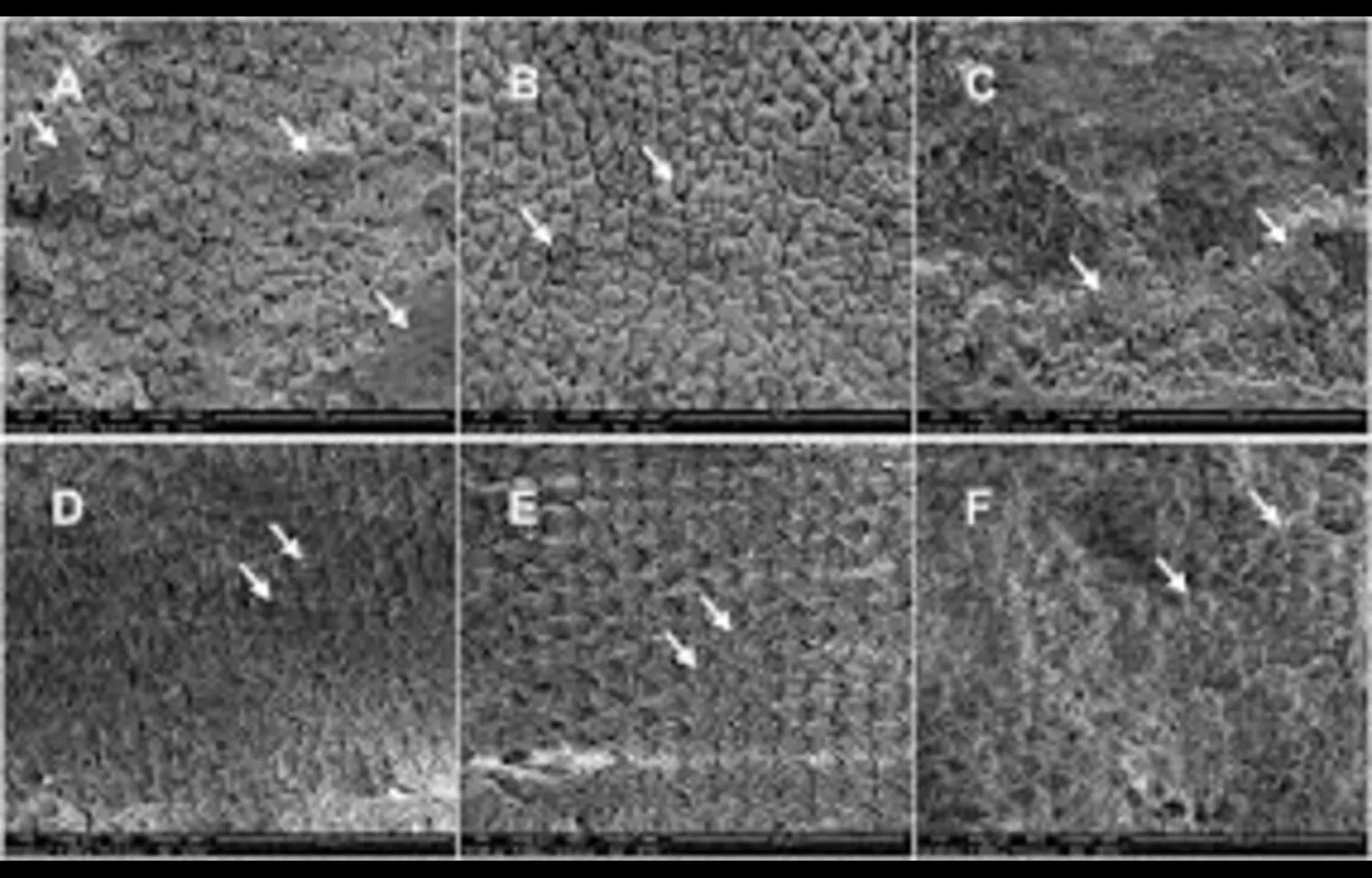
For this study participants were selected from 2 general practice clinics in Victoria, Australia, who were between the ages of 45 and 70 and had recently completed all or part of a CVD risk assessment. The participants gave their assent, underwent retinal imaging with an automated fundus camera, and a deep learning system produced a rpCVD risk score. The World Health Organization’s (WHO) CVD risk score, which takes into account clinical risk variables including age and sex, was compared to this score.
Using data from the UK Biobank, the prediction accuracy of the WHO CVD risk scores and rpCVD risk scores for 10-year incident CVD occurrences was examined. The accuracy of each system was measured using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC). A survey was used to gauge participant satisfaction, and the proportion of people having pictures good enough to generate a rpCVD risk score was used to calculate the imaging success rate.
A 93.9% imaging success rate was achieved by assigning a rpCVD risk score to 339 out of the 361 individuals. There was a moderate association between the WHO CVD risk scores and the rpCVD risk scores.
In spite of this, the WHO CVD risk score (AUC = 0.693, 95% CI: 0.680-0.707) and the rpCVD system, which only uses retinal pictures, showed comparable accuracy in predicting 10-year incident CVD (AUC = 0.672, 95% CI: 0.658-0.686). Nearly, 87.5% of general practitioners (GPs) and 92.5% of participants expressed satisfaction with the system, indicating high levels of satisfaction.
Using just retinal photos, the automated rpCVD system showed predicted accuracy on par with the WHO CVD risk score, which takes into account a number of clinical parameters, including age, which is the most heavily weighted factor for predicting CVD. Overall, the automated rpCVD screening method is viable and well accepted in Australian primary care, as this study shows.
Source:
Hu, W., Lin, Z., Clark, M., Henwood, J., Shang, X., Chen, R., Kiburg, K., Zhang, L., Ge, Z., van Wijngaarden, P., Zhu, Z., & He, M. (2025). Real-world feasibility, accuracy and acceptability of automated retinal photography and AI-based cardiovascular disease risk assessment in Australian primary care settings: a pragmatic trial. Npj Digital Medicine, 8(1), 122. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-025-01436-1
Powered by WPeMatico