Higher oxidative balance score linked to increased odds of allergic rhinitis
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
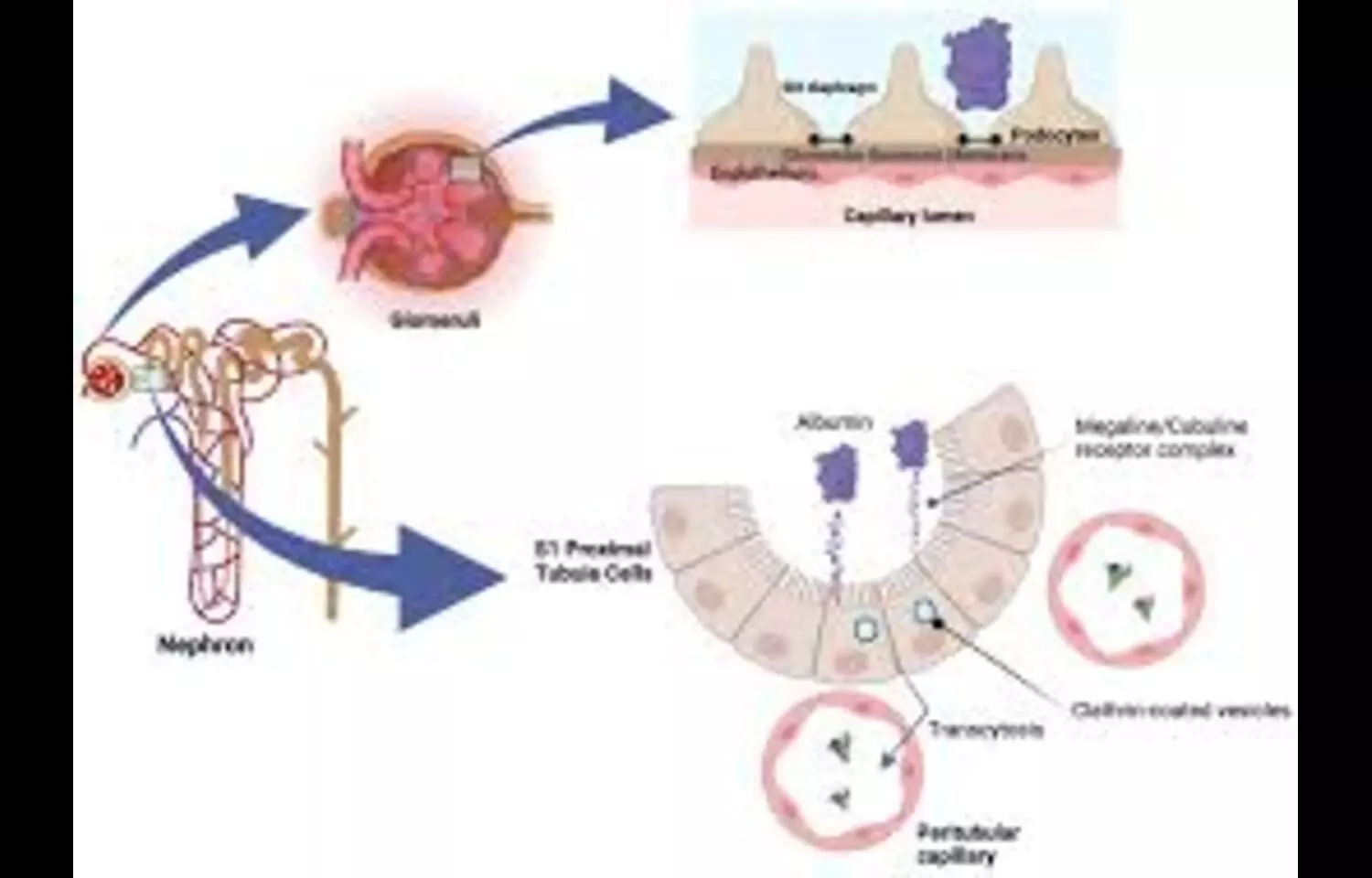
A recent analysis published in BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care revealed that reducing albuminuria plays a crucial role in improving long-term outcomes for patients living with chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus. The study demonstrated that patients who achieved a sustained decrease of more than thirty percent in the urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio over a period of six to twenty-four months experienced significantly lower risks of death, cardiovascular events, and kidney disease progression. These results highlight that albuminuria is not only a marker of kidney damage but also a modifiable treatment target capable of influencing overall survival.
Powered by WPeMatico
