AI could soon detect early voice box cancer from the sound of your voice
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
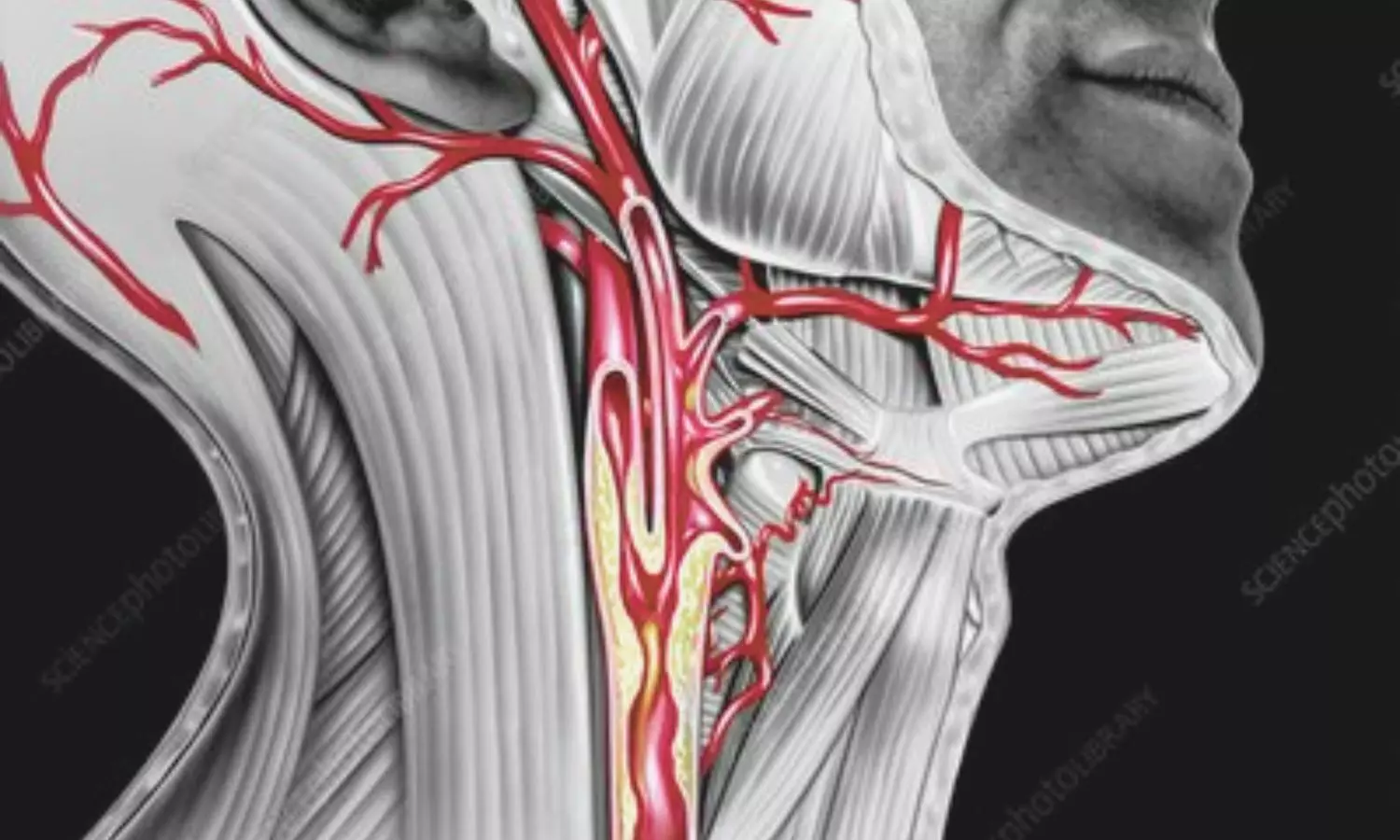
China: A prospective cohort study published in BMJ Open has revealed a strong link between long-term atherogenic index of plasma (AIP) levels and the development and progression of carotid atherosclerosis (CAS). The research, conducted by Hui Li and colleagues from the Department of Health Management Center, Hunan Provincial People’s Hospital, highlights the potential of AIP as an important biomarker for identifying individuals at higher risk of subclinical atherosclerosis.
The study followed 528 adults who underwent annual health examinations over three years from January 2019 to December 2021. Participants were divided into quartiles based on their AIP levels, and carotid atherosclerosis was evaluated using high-resolution ultrasonography. CAS progression was defined as the appearance of new carotid plaques or a significant increase in carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) compared to baseline measurements.
The notable study findings were as follows:
The analysis demonstrated that the relationship between AIP and CAS risk followed an approximately linear pattern, reinforcing the importance of monitoring AIP over time. According to the authors, these findings suggest that tracking changes in AIP trajectories during routine health check-ups could help identify individuals at heightened risk earlier, allowing for preventive strategies to be implemented before significant vascular damage occurs.
The researchers emphasized that AIP, a marker derived from triglyceride and HDL cholesterol levels, could serve as a cost-effective and easily accessible tool in cardiovascular risk assessment. “Regular monitoring of AIP trends may provide valuable insights for early detection of carotid atherosclerosis and guide targeted interventions,” they noted.
Despite its strengths, including the use of a three-year follow-up and trajectory-based analysis, the study had certain limitations. Being a single-center investigation, the findings may not fully represent broader or high-risk populations. The absence of data on lifestyle factors, inflammatory markers, and genetic variables also restricts the understanding of underlying mechanisms. Furthermore, as all participants were from China, applicability to other ethnic or demographic groups may be limited.
“Nevertheless, the study emphasizes the value of incorporating AIP into regular health assessments. By identifying individuals with persistently high or rising AIP levels, clinicians may be able to intervene earlier to prevent or slow the development of carotid atherosclerosis, ultimately reducing the risk of cardiovascular events such as stroke and heart attack,” the authors concluded.
Reference:
Li H, Duan J, Chen J, Tan C, Hu C, Peng J. Association between long-term atherogenic index of plasma and carotid atherosclerosis: a prospective cohort study of a health examination population. BMJ Open. 2025 Jul 30;15(7):e098874. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2025-098874. PMID: 40738628.
Powered by WPeMatico

Researchers have found in a new study that pregnancy-associated acute kidney injury poses a major risk to maternal health in low- and middle-income countries. Therefore strengthening prevention strategies for common causes and expanding antenatal care access can help minimize harmful effects on both mothers and babies. The study was published in the journal of Bull World Health Organ by Tran PNT and colleagues.
The review summarised data from 43 studies, and 40 of these went into the final meta-analysis. Search databases covered Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, Embase, Google Scholar, OvidMedline, ProQuest, and Scopus for studies published between 2013 and 2025. Exclusively, the studies based on the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) diagnostic criteria were considered for statistical pooling. The study also performed subgroup analysis and meta-regression to assess factors underlying heterogeneity in results.
Key findings
The combined incidence of PA-AKI was 91 cases per 10,000 pregnancies (95% CI: 63–133).
The incidence was highest in World Health Organization African Region studies, where it was 254 per 10,000 pregnancies (95% CI: 152–421).
These results indicate that the burden of PA-AKI is unevenly distributed and is heavily dependent on regional healthcare infrastructure and maternal health resources.
The condition was linked to high maternal and neonatal mortality.
The fatality of the case was 10.8% (95% CI: 7.6–15.3), and death during neonatal life or stillbirth resulted in 29.8% of the cases (95% CI: 24.2–36.1).
Additionally, mothers with PA-AKI had an 18.8 times increased risk of maternal death (95% CI: 10.0–35.5) compared to those without the condition, and there was a 4.6 times increased risk (95% CI: 2.1–10.0) of poor fetal outcomes, such as preterm birth and low birth weight.
Pre-eclampsia emerged as the most common cause of PA-AKI, at 44.1% of the cases, followed by hemorrhage (26.2%) and sepsis (16.5%).
These etiologies underscore the preventable nature of most cases of PA-AKI through early obstetric intervention, infection control, and enhanced maternal monitoring during pregnancy.
The research points to the fact that PA-AKI is a significant public health threat among LMICs, with a high risk of mortality for both mother and fetus. Interventions targeted specifically towards public health programs and strengthened maternal healthcare facilities can go a long way toward mitigating incidence and outcomes of PA-AKI in low-resource environments.
Reference:
Tran, P. N. T., Wannakittirat, A., Luyckx, V., Wiles, K., Yadla, M., Chakravarthi, R., Ostermann, M., Wu, V. C., Mehta, R. L., & Srisawat, N. (2025). Incidence of pregnancy-associated acute kidney injury in low- and middle-income countries: a meta-analysis. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 103(8), 493–506. https://doi.org/10.2471/BLT.24.293077
Powered by WPeMatico
