Smoking and periodontitis relevant risk indicators of peri-implantits, finds study

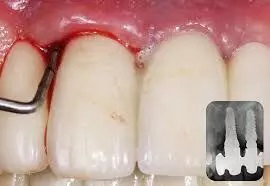
Smoking and periodontitis are relevant risk indicators of peri-implants, finds a study published in the Clinical Oral Implants Research.
The primary aim of this study was to investigate the prevalence of peri-implant diseases in a randomly selected Norwegian population. The secondary aims were to explore risk indicators for peri-implant diseases and to validate self-reported outcome measures from a survey with clinical parameters. Patients (n = 3083) rehabilitated with dental implants in 2014 were mailed a questionnaire and invited to a clinical examination. A randomly selected subset of responders underwent a clinical examination (n = 242). Full mouth clinical and radiographic examinations were conducted. Multiple logistic regression was used to assess patient-related risk indicators for peri-implantitis. Self-reported data were compared with data from the clinical examination using Spearman correlation and binary logistic regression. Results: The prevalence of peri-implantitis was 17.0% at patient level and 8.6% at implant level, according to the 2018 classification. Risk indicators for peri-implantitis included smoking and periodontitis in the adjusted model. The correlation was strong (r = 0.91, p < 0.001) between number of self-reported implants and clinical counts, whereas self-reported peri-implant inflammation was associated with peri-implantitis (OR 6.4 [95% CI 3.0, 13.7]). Smoking and periodontitis were identified as key risk indicators for peri-implantitis. Questionnaire data rendered clinically valid estimates of implant number, and self-reported peri-implant inflammation was associated with clinical peri-implantitis.
Mauland, E., Sørensen, K., Aarbu, N., Verket, A., Ellingsen, S., Bull, V., Gaarden, R., Lie, S. and Bunæs, D. (2024), A Cross-Sectional Study of Peri-Implant Diseases in a Random Norwegian Population: Prevalence, Risk Indicators, and Clinical Validation of Patient-Reported Outcomes. Clin Oral Impl Res. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.14371
Keywords:
Smoking, periodontitis, relevant, risk, indicators, peri-implantits, finds, study, Mauland, E., Sørensen, K., Aarbu, N., Verket, A., Ellingsen, S., Bull, V., Gaarden, R., Lie, S. and Bunæs, D.