Photogrammetric Systems Outperform Traditional and Intraoral Methods in Impression Accuracy in full-arch dental implant rehabilitation: Study
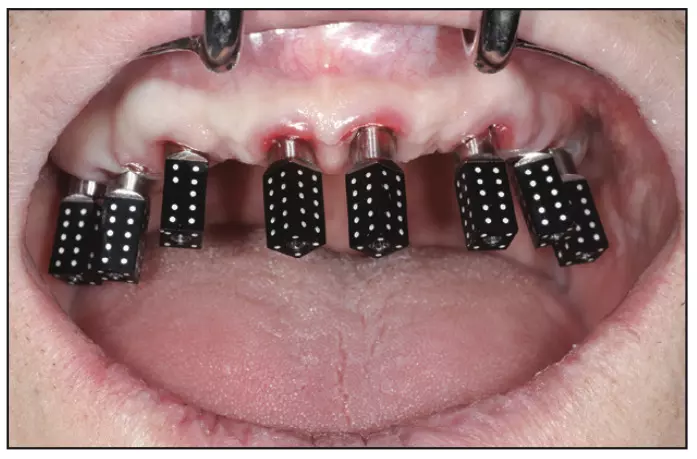
Researchers have found in a new study that Icam4D and PIC photogrammetric impression systems showed the highest accuracy, surpassing conventional impression techniques in in full-arch dental implant rehabilitation.Further it was found that intraoral scanning method was least accurate.
A study was done to compare the accuracy of photogrammetric imaging, intraoral scanning and conventional impression technique in full-arch dental implant rehabilitation. A resin edentulous mandibular model with six parallel implants was fabricated as master model. And three impression groups were performed: conventional splinted open tray impression technique (CON, n = 10); intraoral scanning technique with 3 Shape scanner (IOS, n = 10; TRIOS3, 3 Shape); digital photogrammetry impression technique with two different photogrammetric system namely PG-1 (Icam4D) and PG-2 (PIC) groups (n = 10). The reference values of master model and test values of CON group were digitized with a laboratory reference scanner, and for all groups the STL files were exported for analyzation. The differences in trueness and precision among the three groups were analyzed using reverse engineering software, focusing on three-dimensional (3D) linearity, angularity, and root mean square (RMS) deviations. Results: For trueness, median deviations (μm) for CON, IOS, PG-1, and PG-2 were 66.05, 78.58, 25.23, and 28.15, with angle deviations of 0.35°, 0.52°, 0.12°, and 0.14°, and RMS deviations (μm) of 40.50, 91.75, 10.87, and 13.35, respectively. Significant differences in X, Y-axis, 3D linearity, angularity, and RMS deviations among groups (p < 0.01). For precision, linear deviations (μm) were 39.32, 45.33, 15.80, and 17.78, with angle deviations of 0.24°, 0.38°, 0.10°, and 0.13°, and RMS deviations (μm) of 36.55, 82.8, 3.7, and 4.6, respectively. Significant differences in X, Y-axis, 3D linearity, XZ-plane, and RMS deviations among groups (p < 0.05). The Icam4D and PIC photogrammetric impression systems exhibited the highest levels of accuracy, followed by conventional impression techniques, whereas intraoral scanning techniques demonstrated the least accuracy.
Reference:
Abuduwaili, K., Huang, R., Song, J. et al. Comparison of photogrammetric imaging, intraoral scanning and conventional impression accuracy of full-arch dental implant rehabilitation: an in vitro study. BMC Oral Health 25, 753 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-025-06029-8
Keywords:
BMC Oral Health, Photogrammetry, Digital impression, Edentulous, Accuracy, Abuduwaili, K., Huang, R., Song, J.
