HCQ Plus Prednisolone Improves Outcomes in Inflammatory Cardiomyopathy: Study
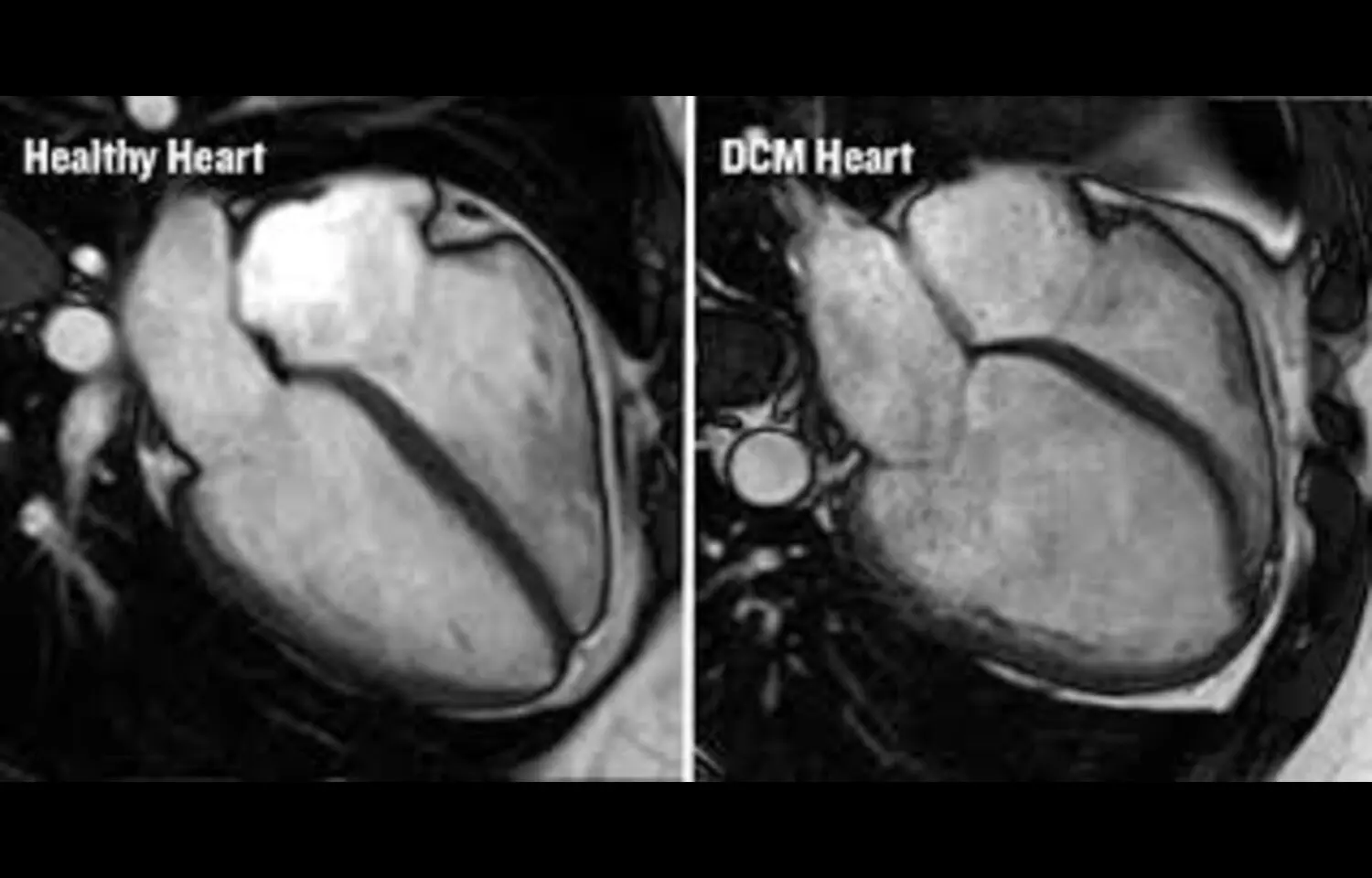
Inflammatory cardiomyopathy, often following fulminant myocarditis, is characterized by myocardial inflammation, impaired cardiac function, and increased risk of heart failure. Effective management of this condition is essential to prevent long-term complications and improve patient survival. Traditional treatment approaches often focus on supportive care, but recent research has explored immunomodulatory therapies to directly target inflammation and preserve cardiac function.
A new study investigated the efficacy of a 12-month combination therapy with hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) and prednisolone in patients diagnosed with inflammatory cardiomyopathy. The study included patients who had experienced fulminant myocarditis and demonstrated reduced left ventricular function, elevated inflammatory markers, and clinical symptoms of heart failure. The intervention group received HCQ alongside a tapering regimen of prednisolone, while outcomes were monitored through cardiac imaging, laboratory markers, and patient-reported functional status.
Results showed that combination therapy significantly improved cardiac function, as measured by increased left ventricular ejection fraction and reduced ventricular dilation. Inflammatory markers, including C-reactive protein and cytokine levels, were markedly reduced, indicating effective suppression of myocardial inflammation. Patients also reported improved exercise tolerance and reduced fatigue, suggesting enhanced quality of life. Importantly, the treatment was well tolerated, with no serious adverse events reported, highlighting the potential safety of long-term HCQ and prednisolone therapy in this population.
The authors note that while these findings are promising, larger multicenter studies with longer follow-up are needed to confirm efficacy, optimize dosing, and fully evaluate long-term safety. Nevertheless, the study provides strong preliminary evidence that combining HCQ with prednisolone can be an effective strategy to manage inflammatory cardiomyopathy following fulminant myocarditis, addressing both inflammation and cardiac function.
Keywords: hydroxychloroquine, prednisolone, inflammatory cardiomyopathy, fulminant myocarditis, heart function, cardiac inflammation, immunomodulatory therapy, left ventricular ejection fraction, heart failure, Journal of Cardiac Failure, He, W., Cui, G., Chen, J



