Older Native Americans may experience higher levels of cognitive impairment than previously thought
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Powered by WPeMatico
Researchers have found in a recent study that in patients with sepsis, treatment with piperacillin-tazobactam was associated with a 5 percent increase in 90-day mortality, more days on a ventilator, and more time with organ failure compared to Cefepime.
The study conducted at the University of Michigan analyzed in depth regarding the antibiotic treatment for bacterial sepsis and revealed the potentially negative consequences associated with the empirical use of certain antibiotics. The key findings of this study were published in the recent issue of the Journal of American Medical Association – Internal Medicine.
The study scrutinized the outcomes of patients treated empirically for sepsis with two commonly used antibiotics, the piperacillin-tazobactam and cefepime. Previous studies had hinted at adverse outcomes associated with the use of antianaerobic antibiotics like piperacillin-tazobactam, when compared to the anaerobe-sparing antibiotics like cefepime. However, the most recent investigation by Rishi Chanderraj and colleagues was undertaken to provide clear insights into this matter.
This study analyzed data that spanned from July 2014 to December 2018 and examined over 7,500 hospital admissions, including a 15-month period characterized by a shortage of piperacillin-tazobactam. The patients treated with either piperacillin-tazobactam or cefepime for sepsis were included in the study.
Despite the previous observations that suggest no significant difference in short-term outcomes, this study uncovered a strong reality. When administered empirically, piperacillin-tazobactam was associated with higher mortality rates and prolonged organ dysfunction than cefepime. These results imply that the widespread empirical use of antianaerobic antibiotics in sepsis treatment might harbor unintended harm.
This study utilized an instrumental variable analysis by leveraging the piperacillin-tazobactam shortage period as a tool to reduce the potential confounding factors. This meticulous approach provided robust evidence for the adverse effects associated with piperacillin-tazobactam use in sepsis treatment.
Given the critical nature of sepsis management, these findings suggest that clinicians must cautiously consider the choice of antibiotics. While the broad-spectrum coverage may seem appealing, this study illuminates the importance of weighing the risks and benefits associated with the selection of empirical antibiotics.
Further research and comprehensive analysis are imperative to highlight the optimal antibiotic strategies for sepsis management. Refining the treatment protocols based on the comprehensive evidence would help in improving the patient outcomes and reducing the potential harm. It is obvious that a precise approach to antibiotic selection in sepsis treatment is essential. The outcomes of this study can help in prioritizing patient safety and efficacy which can in turn aid better navigation of this complex terrain with great precision.
Source:
Chanderraj, R., Admon, A. J., He, Y., Nuppnau, M., Albin, O. R., Prescott, H. C., Dickson, R. P., & Sjoding, M. W. (2024). Mortality of Patients With Sepsis Administered Piperacillin-Tazobactam vs Cefepime. In JAMA Internal Medicine. American Medical Association (AMA). https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2024.0581
Powered by WPeMatico
A recent retrospective study investigated the correlation between elevated blood glucose levels and postoperative complications in diabetic patients who underwent surgical treatment for torsional ankle fractures. The findings of this study published in the Foot and Ankle International journal highlighted a significant association between high HbA1c levels and adverse outcomes following surgery.
This study spanned from January 2017 to December 2021 involved a thorough examination of consecutive diabetic patients who underwent surgical intervention for ankle injuries. The patients were categorized into two groups based on their HbA1c levels, where one group had patients with levels above 7.0% and were classified as the high-HbA1c group, while the other group had patients with levels equal to or below 7.0% that constituted the low-HbA1c group. A intense propensity score match was executed to reduce the potential confounding factors.
Among the matched cohort of 238 patients that comprised 119 individuals in each group, strong disparities in postoperative outcomes were observed. The patients with high HbA1c levels expressed a significantly higher incidence of complications (31.1% vs. 18.5%) and unplanned secondary procedures (22.7% vs. 8.4%) when compared to their counterparts with lower HbA1c levels.
The multivariate analyses further underlined the adverse impact of increased HbA1c levels on surgical outcomes. The patients with high HbA1c levels were found to be at substantially greater risk of undergoing any complications, superficial and deep infections, as well as requiring unplanned secondary operations, even after accounting for potential confounders.
The implications of these findings highlight the importance of glycemic control in diabetic patients who undergo surgical treatment for ankle fractures. The multivariate linear regression analyses revealed a direct correlation between high HbA1c levels and both the frequency of complications and the necessity for secondary procedures which highlights the need for vigilant preoperative glycemic management.
The outcomes of this study emphasized the potential for optimizing patient outcomes through targeted interventions to control blood glucose levels prior to surgery. This research observed that meticulous preoperative assessment and management of glycemic control could reduce the risk of postoperative complications and enhance the overall success of surgical interventions for ankle fractures in diabetic patients. Overall, the study provides strong evidence of the detrimental impact of high blood glucose levels on the postoperative course of diabetic patients undergoing surgical treatment for torsional ankle fractures.
Source:
Chen, D., Liu, S., Liu, P., & Song, W. (2024). Effect of Elevated Blood Glucose on Postoperative Complications Among Diabetic Patients After Surgical Treatment of Torsional Ankle Fracture. In Foot & Ankle International. SAGE Publications. https://doi.org/10.1177/10711007241250005
Powered by WPeMatico

A recent study conducted in Bangladesh highlights the crucial role of maternal vitamin D supplementation to prevent infantile rickets in regions lacking routine infant vitamin D supplementation. This secondary analysis published in the Pediatrics journal revealed strong findings regarding the dosage and timing of vitamin D supplementation.
In low- and middle-income countries where routine infant vitamin D supplementation is not standard practice, the concerns regarding infantile rickets have remained. Rickets is a softening and weakening of bones in children that leads to serious health complications if left untreated. And so, Maria-Elena Lautatzis and colleagues investigated the impact of maternal vitamin D supplementation on infantile rickets risk.
The study included a total of 1300 pregnant women who were randomized into various groups receiving different doses of vitamin D supplementation or placebos. The supplementation regimens ranged from 4200 IU to 28,000 IU per week and was administered from the second trimester of pregnancy until delivery and continued postpartum.
Also, the infants born to these women underwent biochemical screening for rickets between 6 to 12 months of age. The results were promising, that among the 790 infants screened, approximately 4.9% were diagnosed with biochemical rickets. Which observed the highest prevalence of rickets in the placebo group, at 7.8%.
However, infants born to mothers who received a high dosage of vitamin D supplementation (28,000 IU/week) during the third trimester of pregnancy until 6 months postpartum expressed a significantly lower risk of developing biochemical rickets. The risk was reduced to just 1.3% in this group by highlighting the potential efficacy of this supplementation regimen.
Infants whose mothers received only prenatal supplementation at varying doses showed no significant difference in rickets risk when compared to the placebo group. These findings underline the importance of both the dosage and timing of maternal vitamin D supplementation in reducing the risk of infantile rickets. The outcomes of this study emphasize the need for further investigation to determine the optimal dosage and duration of postpartum vitamin D supplementation, especially during lactation. These findings have significant implications for public health policies in regions where infantile rickets remains a concern. Overall, the study illuminates the critical role of maternal vitamin D supplementation in reducing the risk of infantile rickets in regions without routine infant supplementation programs.
Reference:
Lautatzis, M.-E., Keya, F. K., Al Mahmud, A., Tariq, U., Lam, C., Morris, S. K., Stimec, J., Zlotkin, S., Ahmed, T., Harrington, J., & Roth, D. E. (2024). Maternal Vitamin D Supplementation and Infantile Rickets: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Trial. In Pediatrics. American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP). https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2023-063263
Powered by WPeMatico
Researchers in a recent study have sought to enhance risk prediction for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) by evaluating the prognostic value of various cardiovascular biomarkers in addition to established risk factors. Identifying individuals at high risk for ASCVD is crucial for informing primary prevention strategies. However, their impact is more significant for heart failure and mortality outcomes, particularly in older adults. This study was published in JAMA by Neumann JT and colleagues.
The study included individuals with a median age of 53.1 years, of whom 52.4% were women, with a median follow-up of 11.8 years. Incidence of ASCVD events totaled 17,211 cases during the follow-up period. Each biomarker showed a significant association with ASCVD and secondary outcomes. Addition of biomarkers to established risk factor models led to a small improvement in risk prediction metrics for ASCVD but had a more pronounced impact on heart failure and mortality outcomes, particularly in individuals aged 65 years or older.
The key findings of the study were as follows:
The study analyzed data from 164,054 individuals across 28 population-based cohorts from 12 countries and 4 continents.
All biomarkers, including high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I, high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide, B-type natriuretic peptide, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, were significantly associated with incident ASCVD events and secondary outcomes such as all-cause mortality, heart failure, ischemic stroke, and myocardial infarction.
Addition of each biomarker to established risk factor models improved the C statistic, with the combination of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein showing the most substantial improvement in risk prediction for ASCVD, particularly in younger adults aged <65 years.
However, the incremental value of biomarkers in improving risk prediction metrics for ASCVD was modest, although more favorable for heart failure and mortality outcomes.
While cardiovascular biomarkers were strongly associated with fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events and mortality, their addition to established risk factors only marginally improved risk prediction for ASCVD. However, the incremental value of biomarkers was more pronounced for heart failure and mortality outcomes. These findings suggest that while biomarkers may offer some additional predictive value, their impact on overall risk prediction for ASCVD is limited, particularly in younger adults.
Reference:
Neumann JT, Twerenbold R, Weimann J, et al. Prognostic Value of Cardiovascular Biomarkers in the Population. JAMA. Published online May 13, 2024. doi:10.1001/jama.2024.5596
Powered by WPeMatico
India: In a recent breakthrough study published in the Journal of the Association of Physicians of India, researchers have
uncovered a significant association between Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
(DPN) and micronutrient deficiencies. Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy, a common
complication of diabetes, affects millions worldwide, causing pain, numbness,
and weakness, primarily in the extremities. This research sheds light on the
potential role of micronutrients in mitigating the risk and severity of DPN,
offering new avenues for prevention and treatment strategies.
The study revealed
that altered levels of trace elements have a role in the pathogenesis and
progression of diabetes mellitus (DM). They also play a significant role in
diabetes complications, especially diabetic neuropathy.
Diabetes
mellitus is a common metabolic disorder that has been defined by hyperglycemia.
Diabetic patients usually have high oxidative stress levels. Mitochondrial
dysfunction and blood vessel inflammation are associated with a greater
requirement for micronutrients in diabetic patients. These micronutrients may
have an association with complications in patients with diabetes.
Sandhya
Gautam, Lala Lajpat Rai Memorial Medical College, Meerut, Uttar Pradesh, India,
and colleagues aimed to show the association of diabetic peripheral neuropathy
with levels of micronutrients such as zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), vitamin B 12 (Vit
B 12 ), and magnesium (Mg).
For this purpose, the researchers conducted a
cross-sectional study in the Department of Medicine, Lala Lajpat Rai Memorial
Medical College, Meerut. The study included 130 randomly selected
cases of confirmed type-2 diabetic patients. DPN cases were identified using
the Michigan neuropathy screening instrument. Out of 130 diabetic patients, 28
patients had diabetic neuropathy. The level of various micronutrients was
assessed and correlated with DPN development.
The researchers revealed that the association of DPN with
Zn and Vit B12 was found to be significant, whereas Cu and Mg were found to be
insignificant.
The decreased
blood levels of Mg, Zn, and Vit B 12 and increased blood levels of Cu, as have
been found in the present study, can be utilized for diabetes management.
“However, these
observations require further research because of the important role of trace
elements in DM; it is suggested that an adequate supply of these substances in
the diet of patients with diabetes can be beneficial in the long-term
management of diabetic patients, and further study in this field is
recommended,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers noted that since it was a cross-sectional
study, follow-up of the patients could not be done. Other limitation of the
study was the small sample size, so the study findings can not be
generalized. So, there is a need for a multicentric study with a larger sample
size so that findings can be generalized.
As the global prevalence of diabetes continues to
rise, understanding the interplay between nutrition and diabetic complications
becomes increasingly vital. This study offers valuable insights into
personalized approaches for DPN management, emphasizing the importance of
comprehensive care that addresses metabolic and nutritional factors in
diabetic patients.
Reference:
Gautam S, Mittal C, Ranjan A, et al. Association
of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy with Micronutrients. J Assoc Physicians India
2024;72(5):65-67.
Powered by WPeMatico

Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome characterized by high mortality and frequent hospitalizations. HF significantly affected the quality of life, especially in individuals > 60 years of age . According to epidemiologic statistics, HF patients number 80 million worldwide, with China reporting an HF prevalence of 13.7 million among adults in 2015 . The prevalence of HF poses a growing health and economic burden on individuals and society [3]. Despite notable progress in drug treatments for HF, especially in heart failure patients with a reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), challenges in treatment persist .
Announcing a new publication for Acta Materia Medica journal. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors are a class of glucose-lowering drugs known for robust cardiovascular protective properties. However, the side effects induced by Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition limit application in cardiovascular medicine.
Prior research showed that thoughtful structural modifications can dissociate the anti-heart failure activity from glucose-lowering effects. Moreover, it was shown that the glyceraldehyde derivative, JX22, developed by scaffold hopping from empagliflozin, exhibits a superior cardiomyocyte protective effect, albeit with increased cytotoxicity compared to empagliflozin.
In this study systematic structural modifications of JX22 were performed to enhance anti-heart failure efficacy and safety, while reducing glucose-lowering activity. Twenty glyceraldehyde-based derivatives were synthesized and compound 12 emerged as an optimal candidate by exhibiting an improved cytoprotective effect compared to JX22. Compound 12 significantly inhibited the activity of NHE1 on the myocardial membrane, thereby maintaining intracellular ion homeostasis. In vivo efficacy results demonstrated that compound 12 at 10 mg/kg significantly ameliorated cardiac dysfunction, myocardial fibrosis, and exercise tolerance in isoproterenol-induced heart failure mice without a glucose-lowering effect. Furthermore, compound 12 exhibited favorable safety profiles in single-dose toxicity and hERG inhibition tests, along with promising pharmacokinetic properties in mice.
This study not only underscores the potential of compound 12 for further investigation but also highlights the effectiveness of the scaffold hopping strategy.
Reference:
Xiao Li, Yue Yao and Luoyifan Zhou et al. Glyceraldehyde derivatives inspired by empagliflozin as potential anti-heart failure agents independent of glucose-lowering effects. Acta Materia Medica. 2024. Vol. 3(2):133-146. DOI: 10.15212/AMM-2024-0009.
Powered by WPeMatico
UK: A groundbreaking study has unveiled promising insights into the efficacy of Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) screening in reducing prostate cancer mortality over 15 years. The study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) is set to revolutionize the approach to prostate cancer screening and treatment.
The secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial (CAP) comprising 415 357 men aged 50 to 69 found that a single invitation for a PSA screening test reduced prostate cancer mortality at a median follow-up of 15 years, however, the absolute mortality benefit was small, compared with no invitation for routine PSA testing.
“The risk of death from prostate cancer was lower in the group invited to screening (0.69% vs 0.78%; mean difference, 0.09%) versus the control group,” the researchers reported.
Prostate cancer remains one of the most prevalent forms of cancer among men globally, with mortality rates continuing to pose a significant concern. In light of this, the findings from the CAP trial hold immense significance in the realm of cancer research and public health.
The CAP trial reported no effect of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening on prostate cancer mortality at a median 10-year follow-up (primary outcome), however, there is no clarity on the long-term effects of PSA screening on prostate cancer mortality. Therefore, Richard M. Martin, University of Bristol, Bristol, United Kingdom, and colleagues aimed to evaluate the effect of a single PSA screening on prostate cancer-specific mortality at a median 15-year follow-up versus no invitation for screening.
The secondary analysis included men aged 50 to 69 years, identified at 573 primary care practices in England and Wales. Primary care practices were randomized between 2001 and 2007, and enrollment was done between 2002 to 2009.
Men received a single invitation for a PSA screening test with subsequent diagnostic tests if the PSA level was 3.0 ng/mL or greater. The control group received standard practice (no invitation).
The primary outcome was previously reported. Of 8 prespecified secondary outcomes, results of 4 were reported previously. The four remaining were all-cause mortality, prostate cancer-specific mortality, and prostate cancer stage and Gleason grade at diagnosis.
Of 415 357 eligible men (mean age, 59.0 years), the analyses included 98% of men. Overall, 12 013 and 12 958 men with a prostate cancer diagnosis were in the intervention and control groups, respectively (15-year cumulative risk, 7.08%, and 6.94%, respectively).
The study led to the following findings:
“In this secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial, a single invitation for PSA screening versus the standard practice without routine screening reduced prostate cancer deaths at a median follow-up of 15 years. However, there was a small absolute reduction in deaths,” the researchers wrote.
In conclusion, CAP Randomized Clinical Trial findings offer hope in the fight against prostate cancer, reaffirming the critical role of PSA screening in saving lives. Moving forward, continued efforts to enhance screening protocols and promote informed decision-making will be pivotal in advancing prostate cancer care and reducing mortality rates worldwide.
Reference:
Martin RM, Turner EL, Young GJ, et al. Prostate-Specific Antigen Screening and 15-Year Prostate Cancer Mortality: A Secondary Analysis of the CAP Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2024;331(17):1460–1470. doi:10.1001/jama.2024.4011
Powered by WPeMatico
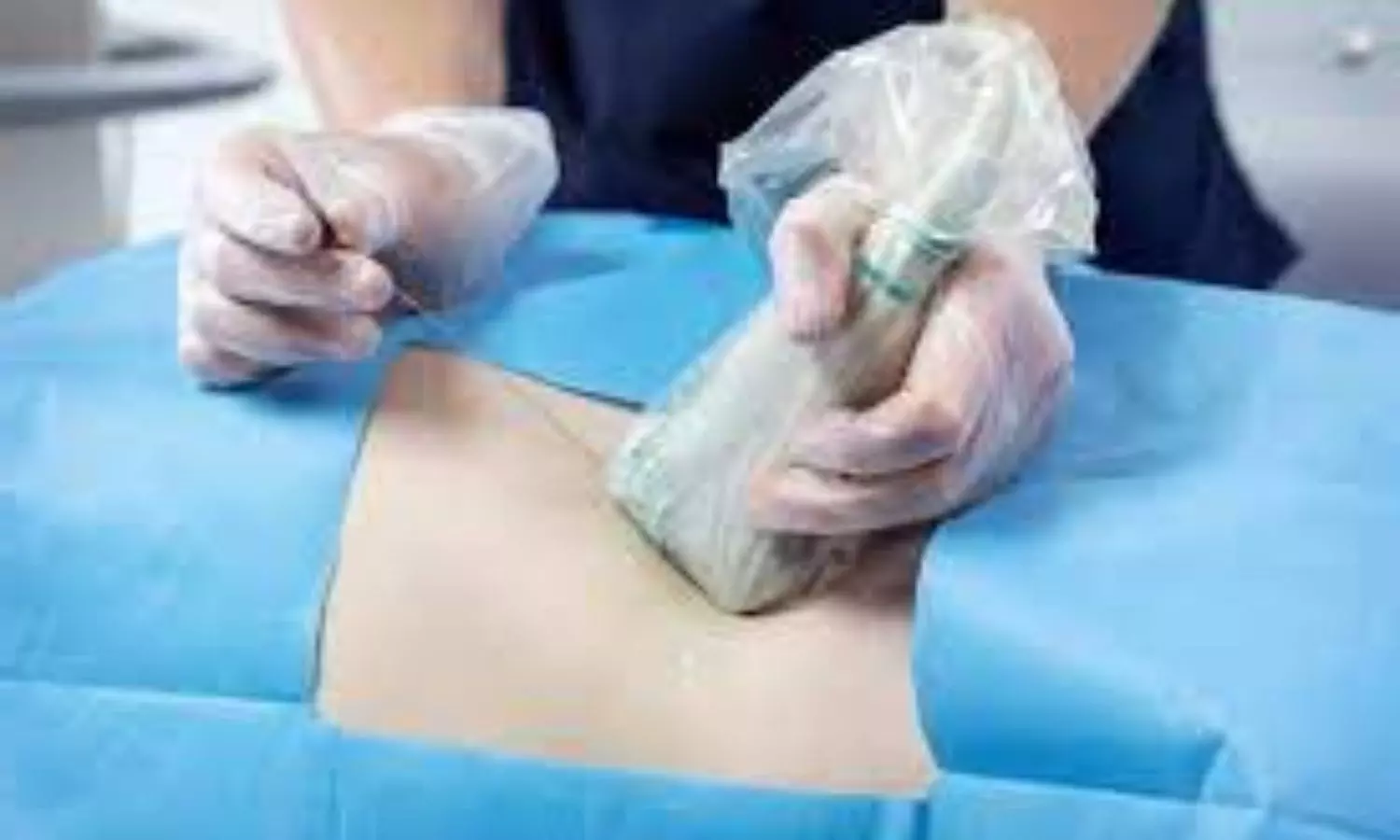
Recent research compared the use of a mixed injection of short-acting lignocaine and long-acting ropivacaine versus undiluted sequential injections for ultrasound-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus block in upper limb surgeries. The primary outcome was the percentage of participants with complete four-nerve sensory blocks at 10 minutes post block injection, and secondary outcomes included sensory and motor block characteristics at 30 minutes, total duration of analgesia, and complications. The study involved a double-blinded randomized trial on 64 adult patients and found that the percentage of participants with a complete four-nerve sensory block at 10 minutes was higher in the sequential injections group (69%) versus the mixed injections group (41%). However, complete sensory and motor block rates were similar at 30 minutes. The block procedure time, total duration of analgesia, and sensory and motor block were similar in both groups. There were no major complications.
Comparison of Drug Mixtures and Sequential Injections
The study investigated the use of mixtures of local anesthetic drugs, specifically short-acting lignocaine and long-acting ropivacaine, for nerve blocks. It compared the block characteristics of these drugs when administered as a mixture versus undiluted sequential injections for ultrasound-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus blocks in upper limb surgeries. The findings indicated that sequential lignocaine-ropivacaine, compared to the mixed injection technique, has a higher initial rate of sensory and motor block onset with a similar total block duration. The study discussed the influence of factors such as dose, pKa, drug deposition close to the nerve, and use of additives on the onset of nerve blocks and reviewed existing literature on the use of sequential injections in regional nerve blocks.
Analysis of Study Findings
It was noted that the percentage of patients with a complete four-nerve sensory block at 10 minutes post injection was significantly higher in the sequential injections group compared to the mixed injections group. However, the total duration of sensory and motor block, as well as the duration of analgesia, was similar in both groups. The study acknowledged a few limitations, such as the inability to extrapolate the findings to the technique of giving mixtures of local anesthetics versus single agent, and the small margins of the time requiring a high measurement frequency of multiple variables.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study found that the sequential injection of lignocaine and ropivacaine has a higher rate of sensory and motor block onset initially, but the difference becomes minimal 30 minutes after block injection. Both groups demonstrated similar total durations of sensory and motor block and duration of analgesia. The findings from this research provide valuable insights into the comparative efficacy of mixed versus sequential injections of local anesthetics for nerve blocks in upper limb surgeries.
Key Points
1. The study compared the use of mixed injection of short-acting lignocaine and long-acting ropivacaine versus undiluted sequential injections for ultrasound-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus block in upper limb surgeries. It involved a double-blinded randomized trial on 64 adult patients, with the primary outcome being the percentage of participants with complete four-nerve sensory blocks at 10 minutes post block injection. Secondary outcomes included sensory and motor block characteristics at 30 minutes, total duration of analgesia, and complications.
2. The findings indicated that the sequential injections group had a higher percentage of participants with a complete four-nerve sensory block at 10 minutes compared to the mixed injections group. However, complete sensory and motor block rates were similar at 30 minutes. The study also compared the block characteristics of the local anesthetic drugs, highlighting that sequential lignocaine-ropivacaine had a higher initial rate of sensory and motor block onset with a similar total block duration when compared to the mixed injection technique.
3. The study concluded that while the sequential injection of lignocaine and ropivacaine had a higher rate of sensory and motor block onset initially, the difference became minimal 30 minutes after block injection. Both groups demonstrated similar total durations of sensory and motor block and duration of analgesia. The research provides valuable insights into the comparative efficacy of mixed versus sequential injections of local anesthetics for nerve blocks in upper limb surgeries.
Reference –
Dhar M, Talawar P, Sharma S, Tripathy DK, Gupta V, Varshney P. A randomised trial comparing block characteristics of a mixture versus sequential injections of lignocaine and ropivacaine for supraclavicular brachial plexus nerve block in patients undergoing upper limb surgery. Indian J Anaesth 2024;68:540-6.
Powered by WPeMatico
